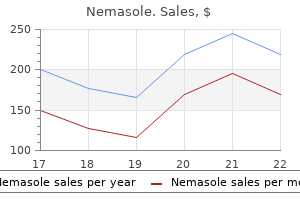
Nemasole
"Cheap nemasole 100mg online, hiv infection rate united states".
X. Giores, M.A.S., M.D.
Co-Director, University of South Alabama College of Medicine
The ultimate purpose of a surveillance programme is to prevent adverse health conditions and their complications highest hiv infection rate by country nemasole 100 mg without prescription. Surveillance data anti virus warning 100mg nemasole overnight delivery, once collected hiv infection prophylaxis guidelines buy 100 mg nemasole with visa, are critical for determination of whether a programme is having any effect hiv infection rates with condom buy discount nemasole 100mg line, evaluation of whether new strategies are necessary, as well as detection of problem areas and intended populations that require more intensive intervention and follow-up. Surveillance of congenital anomalies has been used for one or more of the following purposes: to measure the burden of congenital anomalies and identify high-risk populations; to identify disparities in prevalence and outcomes by factors such as race or ethnicity, maternal age, socioeconomic level or geographic region; to assess the effects of prenatal screening and diagnosis and other changes in diagnostic technologies on birth prevalence; to describe short-term and long-term outcomes of children with congenital anomalies, and to provide information relevant to long-term management of individuals who are affected by serious congenital anomalies; to inform public health and health-care policies and programmes and to plan for needed services among the affected population; to guide the planning, implementation and evaluation of programmes to help prevent congenital anomalies (4) and to minimize complications and adverse outcomes among those affected by congenital anomalies; to assess any additional risk and the nature of adverse outcomes (including congenital anomalies) for fetuses and infants exposed to medicines during pregnancy, to improve management and to inform national and global public health policies (5). Types of surveillance programmes Surveillance programmes can be population based or hospital/facility based and can use active or passive case ascertainment, or can be a hybrid of the two. More information about types of programmes and case ascertainment can be found in Chapter 3. Population-based congenital anomalies surveillance programmes capture birth outcomes with congenital anomalies that occur among a population that is resident in a defined geographical area. Hospital- or facility-based congenital anomalies surveillance programmes capture birth outcomes with congenital anomalies that occur in selected facilities. Sentinel congenital anomalies surveillance programmes are generally set up in one or a few facilities/hospitals, to obtain rapid estimates of the occurrence of an adverse birth outcome. Congenital anomalies: definitions Congenital anomalies comprise a wide range of abnormalities of body structure or function that are present at birth and are of prenatal origin. For efficiency and practicality, 3 the focus is commonly on major structural anomalies. These are defined as structural changes that have significant medical, social or cosmetic consequences for the affected individual, and typically require medical intervention. Major structural anomalies are the conditions that account for most of the deaths, morbidity and disability related to congenital anomalies (see Box 1. In contrast, minor congenital anomalies, although more prevalent among the population, are structural changes that pose no significant health problem in the neonatal period and tend to have limited social or cosmetic consequences for the affected individual. Major anomalies are sometimes associated with minor anomalies, which might be objective. Selected external minor congenital anomalies Absent nails Accessory tragus Anterior anus (ectopic anus) Auricular tag or pit Bifid uvula or cleft uvula Branchial tag or pit Camptodactyly Cup ear Cutis aplasia (if large, this is a major anomaly) Ear lobe crease Ear lobe notch Ear pit or tag Extra nipples (supernumerary nipples) Facial asymmetry Hydrocele Hypoplastic fingernails Hypoplastic toenails Iris coloboma Lop ear Micrognathia Natal teeth Overlapping digits Plagiocephaly Polydactyly type B tag, involves hand and foot Polydactyly type B, of fingers, postaxial Polydactyly type B, of toes, postaxial Preauricular appendage, tag or lobule Redundant neck folds Rocker-bottom feet Single crease, fifth finger Single transverse palmar crease Single umbilical artery Small penis (unless documented as micropenis) Syndactyly involving second and third toes Tongue-tie (ankyloglossia) Umbilical hernia Undescended testicle, bilateral Undescended testicle, unilateral Webbed neck (pterygium colli) When establishing a new congenital anomalies surveillance programme, the initial anomalies that are included can be limited to structural anomalies that are readily identifiable and easily recognized on physical examination at birth or shortly after birth. The list may vary, depending on the capacity and resources of the health-care system and surveillance programme, but typically includes major external congenital anomalies. In some cases, internal anomalies have external manifestations that allow the observer to suspect a particular diagnosis, as is the case with the urethral obstruction sequence. Classification by developmental mechanism or clinical presentation can be important in surveillance, because the same congenital anomaly can have different etiologies. Also, the distinction may be important both clinically and in etiological studies. Please refer to Appendix C for more information about the causes of congenital anomalies and their classification according to developmental mechanism and clinical presentation. Planning activities and tools Many steps are required before conducting surveillance and collecting data. A logic model can be developed to help plan how a programme will be funded and staffed, identify activities and specify short- and- long-term outputs of the surveillance. The planning process would include identifying the existing rules and regulations pertaining to privacy and confidentiality issues surrounding data collection and reporting, and having a protocol in place that addresses handling of privacy and confidentiality. Logic models One approach that can be helpful when planning, implementing and evaluating a congenital anomalies surveillance programme is the use of logic models. A logic model is a graphic representation of how the surveillance programme will work. Logic models can identify what activities are needed, the order in which they would occur, and how the outcomes are going to be achieved. Activities: what activities are required for the surveillance programme to function Expectations: what are the short-term, intermediate, and long-term expectations (or outcomes) for each programme area It is probably best to begin by placing all relevant information into a table format (see Table 2. Sample information to include in a logic model Short- and longterm outcomes Uniform nationwide implementation of the surveillance programme Enhance knowledge Resources Funding sources Activities 1. Develop surveillance system Outputs Institute surveillance system Impact Improved quality of life for affected individuals Reduction in mortality in children aged less than 5 years Reduction in the prevalence of preventable congenital anomalies Infrastructure 1a.
In obstructive sleep apnea antiviral bath order 100mg nemasole fast delivery, a patient will often complain of excessive daytime sleepiness hiv infection symptomatic stage buy discount nemasole 100mg, and the spouse will complain of very loud snoring hiv infection images generic 100 mg nemasole with amex. They have a distortion to their body image hiv urinary infection discount 100 mg nemasole with amex, which is a driving force behind the excessive dieting. Common adverse effects that occur include: Amenorrhea, Electrolyte disturbances, and severe cases can result in cardiac etiologies. Common findings include enlarged parotid glands, enamel erosion, bruised fingers (from sticking them in the mouth), esophageal varices caused by the pressure of vomiting. The two types of operant conditioning are Positive Reinforcement and Negative Reinforcement. Sexual changes such as longer refractory period, delayed ejaculation, slower onset of erection (in men). There are important concepts you must know, and all of the immunologic disorders are fair game on the Step 1 exam. This form of immunization is used when there is a risk of infection and not enough time for the body to develop an ample immune response. When this occurs, the virus cannot infect a cell since the proper genetic materials for this function are absent. As this occurs, severe organ dysfunction ensues, causing damage to the liver, skin, mucosa, and gastrointestinal tract. Hyperacute Rejection: Occurs almost immediately after transplant, whereby preformed anti-donor antibodies cause a response. Chronic Rejection: Occurring months-years post-transplant, is caused by antibody-mediated vascular damage. When it comes to parasites and helminths, your strategy should be memorization of modes of transmission, signs and symptoms, and treatments. Endotoxins cause a wide range of problems through the activation of macrophages and the complement pathway. Coli Vibrio (rice-water stools, highly voluminous) Rotavirus Giardia (foul-smelling) Cryptosporidium Treatment: Triple therapy: Omeprazole, clarithromycin, amoxicillin. Its most popular characteristic is that it produces a fruity-smelling blue-green pigment (due to pyocyanin). Vibrio Cholera causes a rice-water diarrhea by permanently activating the Gs protein.
Psychomotor speed/reaction time Language Memory/learning Visuoperceptual/visuoconstructional Emotion/mood/quality of life Task engagement Sensory-perceptual Wechsler intelligence scales Wechsler intelligence scales attention subtests hiv infection by gender buy 100mg nemasole free shipping. The presence of mesial temporal sclerosis greatly aides in predicting neuropsychological outcome antiviral juice recipe 100 mg nemasole with amex. Knowledge of age of seizure onset and duration of epilepsy can 16 Epilepsy and Seizures 489 be helpful hiv infection french kissing cheap nemasole 100mg amex. Also symptoms of hiv infection in the mouth order nemasole 100 mg on line, carefully watch for abnormal eye movements or episodes in which the patient appears to briefly pause while talking or "space off. Ask the patient if (s)he has experienced a loss of time or if they recall what they were thinking about. Sensory-perceptual examination: the clinical neuropsychologist can evaluate for gross visual field cuts, tactile sensory function (extinction task), simple audition functions, and apraxias. We recommend evaluating for hemi-inattention to visual, auditory, and tactile sensation. Inattention can be rapidly assessed by using a brief bedside bilateral simultaneous stimulation test. One may also assess for finger agnosia, astereognosis, Right/Left orientation, and apraxia. Cranial nerve exam and evaluation of deep tendon reflexes may also assist the neuropsychologist complete the evaluation. Motor examination: Evaluation of grip strength and manual dexterity of both upper extremities is recommended. Neuropsychological psychometric instruments: the selection of instruments should (1) have demonstrated validity (evidence-based) and (2) assist the neuropsychologist to make some statement about the relative risk for neuropsychological impairment following surgery. Ideally, this will include a statement about the type and extent of neuropsychological and psychological impairments that may occur from the proposed surgical procedure. Secondarily, the neuropsychologist may assist with confirming the lateralization or localization of the seizure focus, keeping in mind that this information will be misleading in some patients and assumes normal functional neuroanatomic organization. The neuropsychological measures specified below are guides, and as new tests are developed, neuropsychologists should evaluate the evidence-based research of older and newer instruments, and how new tests may better serve the needs of the patient (Loring and Bauer 2010). Borderline to impaired general cognitive functioning prior to elective surgery could raise concerns about 490 M. The processing speed and working memory indices can be useful for examining the effects of medications, acute seizures, and other transient, acute factors. Academic achievement measures: Including a measure of academic functioning can be helpful, and is often important in academic placement issues for children and adolescents. For children, we recommend a screening of word reading, reading comprehension, spelling and arithmetic skills. Attention/Concentration and "Executive Functions" We recommend an evaluation of simple, focused, and divided attention. In addition, assessment for 16 Epilepsy and Seizures 491 motor impersistence, motor weakness, and personality changes including apathy, social disinhibition, and/or irritability is suggested. Language and Speech: Psychometric evaluation of naming and generative fluency is critical in the evaluation of epilepsy surgery patients. These domains are frequently impaired among patients with epilepsy, and can also be negatively impacted by neurological surgery. Reading and spelling functions may also be assessed, and can also be impacted by some surgical interventions. Inter-ictally, patients with epilepsy rarely exhibit gross aphasia symptoms, but aphasic symptoms post-ictally can predict seizure laterality and seizure outcome (Privetera et al. Learning/Memory: Neuropsychological assessment of declarative memory functions has predictive value of post-surgical memory outcome.

Endoscopic Stages of Esophageal Burns Grade of Injury Normal First degree No erythema Mucosal erythema Effect of Injury Injury Treatment and Outcome No healing time hiv infection methods cheap nemasole 100 mg otc. Second degree Mucosal erythema Noncircumferential exudate Mucosal erythema Circumferential exudate antiviral zdv purchase 100 mg nemasole free shipping. Mucosal erythema Circumferential exudate Esophageal wall perforation Occasionally forms strictures hiv infection per year quality nemasole 100 mg. Larger perforations with surrounding necrosis may require resection with reanastomosis hiv infection cd4 count nemasole 100 mg generic. Tracheoscopy Tracheoscopy should be included to examine the posterior tracheal wall for all third- and fourth-degree injuries. Abortion of Endoscopic Evaluation Endoscopic evaluation should be aborted when there is no definable lumen. Pharmacologic Therapy Gastric reflux precautions, proton pump inhibitors, histamine H2 receptor blockers, or sucralfate should be considered for patients with any mucosal injury. The use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and corticosteroids for secondand third-degree injuries is controversial. No study has proven their effectiveness in preventing stricture formation or other subsequent complications. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are required for symptomatic patients (fever, chest pain, tachycardia) with a known perforation, given their risk of mediastinitis. A nasogastric feeding tube should be placed under direct visualization for all patients with third- and fourth-degree injuries. Although its primary purpose is to allow for adequate nutrition, it also serves as a mechanical stent if left in place throughout reepithelialization. Close observation in a hospital setting is mandatory for all patients with these injuries. Patients with third-degree injuries may attempt a clear diet after 3 days and advance to a regular diet if they remain asymptomatic. A barium or gastrografin swallow study should be repeated after 3 days for all patients with fourth-degree injuries that show clinical improvement before attempting postoperative intake. Further Workup Patients with intentional caustic ingestion should be evaluated and cleared by psychiatry prior to discharge. A baseline barium swallow should be completed 3 weeks post-incident in patients with second-degree injuries or higher. Esophageal Perforation Esophageal perforation may lead to mediastinitis, sepsis, and ultimately death. Patients with esophageal perforations should be monitored closely and treated as discussed previously. Esophageal Strictures Esophageal strictures most commonly occur at the level of the cricopharyngeus, aortic arch, or lower esophageal sphincter. Strictures from caustic ingestion tend to be longer and tighter than benign strictures and may be refractory to and have a higher rate of complications with dilation. One in seven patients may develop malignancy, leading some physicians to advocate for regular esophageal surveillance, although the latent period for development may be as long as 50 years. Nodularity or ulceration in the region of a previously smooth stricture suggests malignant transformation. Conclusion Foreign body aspiration or ingestion and caustic ingestion are serious, potentially life-threatening emergencies. In the course of trauma, foreign bodies, such as chewing gum, teeth, dentures, and other detritus of impact, can be ingested or aspirated, complicating the evaluation and treatment of traumatic injuries. Any difficulties with airway and breathing after traumatic events should raise the specter of possible foreign bodies in the aerodigestive tract, in addition to the other possible etiologies. Caustic ingestions, while not as common as foreign body aspiration/ingestion, can also occur during traumatic episodes, particularly burns and by-products of combustion engines, batteries, and industrial equipment. The most dangerous conditions exist when these emergencies are seen in pediatric patients, as their airways are small and susceptible, and their functional reserves are quite restricted.
