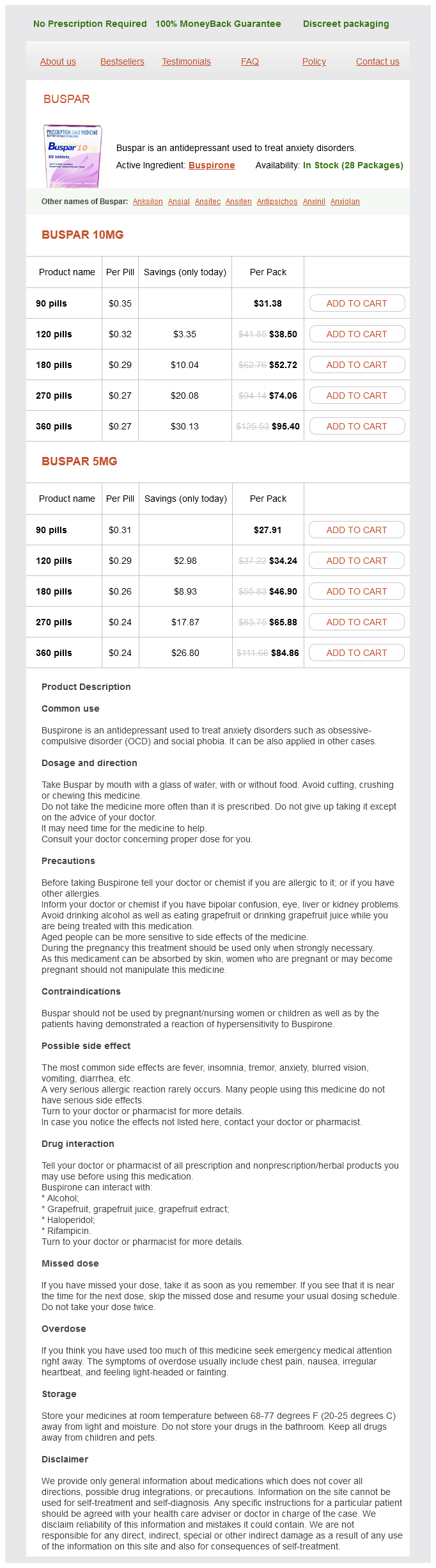
Buspirone
Carl M. Allen, DMD, MSD
- Professor and Director, Division of Oral and Maxillofacial
- Surgery, Pathology, and Dental Anesthesiology
- College of Dentistry, The Ohio State University,
- Columbus, Ohio
Allows the unethical if participants do not development of questions for know they are being observed anxiety questionnaire pdf buy buspirone. Correlational To assess the Allows testing of expected Cannot be used to draw relationships between relationships between and among inferences about the causal and among two or more variables and the making of relationships between and variables predictions anxiety quotes images safe 10mg buspirone. Experimental To assess the causal Allows drawing of conclusions Cannot experimentally impact of one or more about the causal relationships manipulate many important experimental among variables anxiety symptoms women buy buspirone 10 mg low price. Descriptive Research Descriptive research is designed to create a snapshot of the current thoughts anxiety 4 days after drinking buy buspirone 10mg overnight delivery, feelings, or behavior of individuals. This section reviews three types of descriptive research: Case studies, surveys, and observations. Case Study: Sometimes the data in a descriptive research project are based on only a small set of individuals, often only one person or a single small group. More frequently, case studies are conducted on individuals who have unusual or abnormal experiences. A well-known case study is Phineas Gage, a man whose thoughts and emotions were extensively studied after a tamping iron was blasted through his skull in an accident. A representative sample of likely voters would include the same percentages of males, females, age groups, ethnic groups, and socio-economic groups as the larger population. When using naturalistic observation, psychologists observe and record behavior that occurs in everyday settings. For instance, a developmental psychologist might watch children on a playground and describe what they say to each other. One example of laboratory observation involves a systematic procedure known as the strange situation. Descriptive Statistics the results of descriptive research projects are analyzed using descriptive statistics; that is, numbers that summarize the distribution of scores on a measured variable. Most variables have distributions where most of the scores are located near the center of the distribution and the distribution is symmetrical and bell-shaped. A data distribution that is shaped liked a bell in known as a normal distribution. A distribution can be described in terms of its central tendency; that is, the point in the distribution around which the data are centered. They include: the mean or arithmetic average is the most commonly used measure of central tendency. It is computed by calculating the sum of all the scores of the variable and dividing this sum by the number of participants in the distribution. This occurs when there are one or more extreme scores, known as outliers, at one end of the distribution. The single very extreme income has a disproportionate impact on the mean, resulting in a value that does not well represent the central tendency of the data. A final measure of central tendency, known as the mode, represents the value that occurs most frequently in the distribution. In addition to summarizing the central tendency of a distribution, descriptive statistics convey information about how the scores of the variable are spread around the central tendency. The distribution of family incomes is likely to be nonsymmetrical because some incomes can be very large in comparison to most incomes. However, the standard deviation, which is the measure of the approximate average amount scores in a distribution deviate from the mean, is the most commonly used measure of dispersion. Advantages and Disadvantages of Descriptive Research An advantage of descriptive research is that it attempts to capture the complexity of everyday behavior. Case studies provide detailed information about a single person or a small group of people, surveys capture the thoughts or reported behaviors of a large population of people, and observation objectively records the behavior of people or animals as it occurs. Thus, descriptive research is used to provide a relatively complete understanding of what is currently happening. Because there is no comparison group that did not experience the stressful situation, we cannot know what these individuals would be like if they had not had the stressful experience. Correlational Research In contrast to descriptive research, which is designed primarily to provide static pictures, correlational research involves the measurement of two or more relevant variables and an assessment of the relationship among those variables. For instance, the variables of height and weight are correlated because taller people generally weigh more than shorter people. In the same way, study time and memory errors are also correlated, because the more time a person is given to study a list of words, the fewer errors he or she will make. Examples of positive correlations include those between height and weight, education and income, and age and mathematical abilities in children. In each case, people who score higher on one of the variables also score higher on the other variable. In contrast, a negative correlation occurs when values for one variable change in the opposite direction for the other variable. Examples of negative correlations include those between the age of a child and the number of diapers the child uses, and between amount of time studying and the number of errors made on a test. In these cases, people who score higher on one of the variables score lower on the other variable. One way of organizing the data from a correlational study with two variables is to graph the values of each of the measured variables using a scatter plot, a visual image of the relationship between two variables. The Pearson Correlation Coefficient, symbolized by the letter r, is the most common statistical measure of the strength of linear relationships among variables. The direction of the linear relationship is indicated by the sign of the correlation coefficient. The strength of the linear relationship is indexed by the distance of the correlation coefficient from zero. In this example, there is no relationship at all between the two variables, and they are said to be independent. Parts (d) and (e) show patterns of association in which, although there is an association, the points are not well described by a single straight line. Increases in anxiety from low to moderate levels are associated with performance increases, whereas increases in anxiety from moderate to high levels are associated with decreases in performance. He has collected, from a sample of fourth-grade children, a measure of how much violent television each child views during the week, as well as a measure of how aggressively each child plays on the school playground. From his collected data, the researcher discovers a positive correlation between the two measured variables. One alternate possibility is that the causal direction is exactly opposite from what has been hypothesized (see Figure 2. Perhaps children who have behaved aggressively at school develop residual excitement that leads them to want to watch violent television shows at home: Figure 2. It is also possible that both causal directions are operating and that the two variables cause each other (see Figure 2. Parents who use a harsh and punitive discipline style may produce children who both like to watch violent television and who behave aggressively in comparison to children whose parents use less harsh discipline: Figure 2. When the variables are both caused by a third variable, the observed relationship is said to be spurious. If effects of the third variable were taken away, or controlled for, the relationship between the variables would disappear. In the example the relationship between aggression and television viewing might be spurious because by controlling for the effect of the parentsdisciplining style, the relationship between television viewing and aggressive behavior might go away. Third variables in correlational research designs can be thought of as mystery variables because, as they have not been measured, and their presence and identity are usually unknown to the researcher.
Charismatic leaders are leaders who are enthusiastic anxiety heart palpitations purchase generic buspirone from india, committed anxiety symptoms valium treats purchase buspirone 10mg mastercard, and self-confident; who tend to talk about the importance of group goals at a broad level; and who make personal sacrifices for the group anxiety symptoms jaw clenching buy 10 mg buspirone with amex. Charismatic leaders express views that support and validate existing group norms anxiety symptoms gastrointestinal buy buspirone 10 mg without prescription, but that also contain a vision of what the group could or should be. Charismatic leaders use their referent power to motivate, uplift, and inspire others. Another trait-based approach to leadership is based on the idea that leaders take either transactional or transformational leadership styles with their subordinates (Bass, 1999; Pieterse, Van Knippenberg, Schippers, & Stam, 2010). Transactional leaders are the more regular leaders, who work with their subordinates to help them understand what is required of them and to get the job done. Transformational leaders, on the other hand, are more like charismatic leaders as they have a vision of where the group is going, and attempt to stimulate and inspire their workers to move beyond their present status and to create a new and better future. Leaders whose personalities lead them to be more focused on fostering harmonious social relationships among the members of the group, for instance, are particularly effective in situations in which the group is already functioning well, and yet it is important to keep the group members engaged in the task and committed to the group outcomes. Leaders who are more task oriented and directive, on the other hand, are more effective when the group is not functioning well and needs a firm hand to guide it (Ayman, Chemers, & Fiedler, 1995). Personality and Culture Culture greatly affects how individuals perceive themselves, and one important distinction is where a culture falls on the continuum between individualism and collectivism (Vazire, 2014). Individualistic cultures, such as the mainstream culture in the United States, focus on the self more than relationships. Additionally, personality differences typically assessed, such as the Big Five, appear less noticeable in collectivistic cultures. However, within any culture there will be some members who exhibit more individualism than collectivism and vice versa. Personality and Mental Health Although they may appear unrelated, personality traits and mental health disorders are often on a continuum (Twenge & Campbell, 2017). The line between what is considered normal and abnormal is due to the quantity of a trait. When in very high amounts, traits (such as narcissism) can result in a mental health diagnosis. Although clinicians prefer to interpret the patterns themselves, a variety of research has demonstrated that computers can often interpret the results as well as clinicians (Garb, 1998; Karon, 2000). Despite their widespread use, however, the empirical evidence supporting the use of projective tests is mixed. What were the personality characteristics of these people that made them so influential Activities You can complete a self-report measure of personality using a short form of the Five-Factor Personality Test here. Personalities are characterized in terms of traits, which are relatively enduring characteristics that influence our behavior across many situations. Psychologists have investigated hundreds of traits using the self-report approach. The Big Five dimensions are openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. The Big Five are cross-culturally valid and accurately predict some behavior, including work place and academic success, relationships, and psychological disorders. However, psychologists have also found that personality predicts behavior better when the behaviors are averaged across different situations. Personality traits of humans and animals are determined in large part by their genetic makeup. Personality is not determined by any single gene, but rather by the actions of many genes working together. These studies partition personality variability into the interactions among genetics (known as heritability), shared environment, and nonshared environment. In addition to the use of behavioral genetics, our understanding of the role of biology in personality recently has been increased through the use of molecular genetics, the study of which genes are associated with which personality traits in animals and humans. Epigenetic influences are also important in that genes can be expressed through environmental factors. Humanistic theories of personality focus on the underlying motivations that they believed drive personality. Humanists focus on the nature of the self-concept and the development of self-esteem. Abraham Maslow focused on self-actualization as the most advanced motive in his hierarchy of needs, while Carl Rogers focused on how unconditional positive regard helps us reach our full potential. Albert Bandura uses the term reciprocal determinism to explain the complex interactions between individuals, their behavior, and the environment. Objective measures of personality include self-report and informant-rating measures. Additionally, concerns regarding the barnum effect, honeymoon effect, and letter of recommendation effect, are noted. While measures of the Big Five have shown reliability and validity, the Myers-Briggs does not, and therefore, is not a useful measure of personality. Personality is reflected through culture, especially the distinction between individualism and collectivism. Locus of control and attributions for achievement outcomes, Psychological Studies, 31(1), 15-20. Behavioral genetics: An introduction to how genes and environments interact through development to shape differences in mood, personality, and intelligence. Gender differences in personality traits across cultures: Robust and surprising findings. Conscientiousness is the most powerful neurocognitive predictor of school achievement in adolescents. The effect of locus of control and self-esteem on attributions and expectancies after success and failure. Association between novelty seeking and the type 4 dopamine receptor gene in a large Finnish cohort sample. The lexical approach to personality: A historical review of trait taxonomic research. The clinical interpretation of the Thematic Apperception Test, Rorschach, and other clinical data: A reexamination of statistical versus clinical prediction. Linking big personality traits to anxiety, depressive, and substance use disorders: A meta-analysis. Personality in its natural habitat: Manifestations ad implicit folk theories of personality in daily life. A new look at defensive projection: Thought suppression, accessibility, and biased person perception. Validity of observer ratings of the five-factor model of personality traits: A meta-analysis. Socially desirable responding and its elusive effects on the validity of personality assessments. Transformational and transactional leadership and innovative behavior: the moderating role of psychological empowerment. The rank-order consistency of personality traits from childhood to old age: A quantitative review of longitudinal studies. The power of personality: the comparative validity of personality traits, socioeconomic status, and cognitive ability for predicting important life outcomes. The five-factor model and personality disorder empirical literature: A meta analytic review. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Self-other agreement in personality and affectivity: the role of acquaintanceship, trait visibility, and assumed similarity. Personality development in emerging adulthood: Integrating evidence from self and spouse-ratings. This chapter focuses on social psychology, which is defined as the scientific study of how we feel, think, and behave toward the other people around us, and how those people influence our feelings, thoughts, and behavior.
Quality 5 mg buspirone. My Anxiety Disorders Are Gone!!! (Paxil) #TEAMTREES Let’s Change The World!!!!!!!.
Regarding marital status anxiety love buy discount buspirone on-line, 45% of the participants reported to be married (n = 90) anxiety symptoms jittery buy buspirone 5 mg amex, 30 anxiety keeping me up at night purchase buspirone toronto. The data found in this study may be interpreted through different considerations given the reported Haitian national statistics anxiety and nausea buspirone 5mg low price. According to the Haitian Civil Code, the minimum legal age of marriage is 15 for women and 18 for men (Social Institution & Gender Index, n. The increase in marriage rate for young women versus men in Haiti may be due to the fact that some marriages are still arranged or forced, especially in case of rape or pre marital pregnancy (Social Institution & Gender Index, n. This may explain the low percentage of divorce, in addition to the fact that the Haitian population is mainly Catholic. However, this percentage was added to the 45% reported to be married, the sample would represent a paralleled figure at 63. Concerning religions, the majority of the participants reported to be Catholic (n = 138; 69%). The rest of the participants reported to be mainly Protestant (n = 58; 29%), Voodoo practitioner (n = 3; 1. Among the Protestants, there were Adventist, Baptist, Church of God, Methodist, Nazarene, Pentecostal, and Jehovah Witness. It is reported that 80% of the Haitian population are Catholics, whereas 16% are Protestants, 3% practice other form of religions, and 1% practice no religion (NationMaster, n. Nonetheless, the notion of religion in Haiti is far more complex than being affixed under the above-mentioned categories. Voodoo is so pervasive in the Haitian culture, it can be considered as interchangeable with Catholicism (Dash, 2001). The practice of Voodoo has been long stigmatized and associated with the masses or the poor. Yet, the practice has been found to be widely adopted in private among various social classes. Most Haitians have a religion with Voodoo serving as a supplementary religion when it is needed (Colin & Paperwalla, 2013; Vonarx, 2011). Hence, the low percentage of Voodoo practitioners reported in the finding may not reflect the actual data. Concerning family history of prostate cancer, the majority of the participants reported to have no family history of prostate cancer (n = 137; 68. It may due to the fact that they do not have that information because it was not shared or because it is simply unknown. As Colin and Paperwalla (2013) discussed, Haitians are very private concerning their health matters. Many times, health information is kept from other family members, especially, if the health matter is relating to factors that are considered taboo by the culture. In addition, the information may not be known due to the lack of resources that exists in Haiti. Regarding intent to be screened for prostate cancer, the scores were not normally disseminated, triggering the need for a dichotomous rearrangement of the data. More than half of the participants fell under the category of Likely to be screened for prostate cancer category (n = 110, 55%), and the remainder fell under the category Unlikely to be screened for prostate cancer (n = 90, 45%). This finding was perhaps a revelation given the well-known myths related to manhood that are associated with prostate cancer and prostate cancer screening (Cobran et al. Such a practice may be controversial in cultures, including Haitian culture, where homosexuality is taboo (Colin & Paperwalla, 2013; Dash, 2001). Nonetheless, the 10% edge that is reported in this study toward likelihood to be screened for prostate cancer may be due to the submissive nature of Haitians towards authority figures. One of the questions addressing the intent to be screened for prostate cancer had a reinforcing cue (the recommendation of a health care professional). Therefore, it was expected that most Haitians would comply with such a recommendation. Due to the negative skewness of the outcome variable scores, the scores were dichotomized to allow for binary logistic regression in lieu of multiple regression. As a result, this hypothesis now looks at three continuous level data predictors and one dichotomous categorical outcome variable. This finding can be supported by the predictive cross sectional study conducted by Abuadas, Petro-Nustas, and Albikawi (2015). Similar support may be found in the descriptive study by Ghodsbin, Zare, Jahanbin, Ariafar, and Keshayarzi (2013). They investigated the level of knowledge and health beliefs about prostate cancer screening among retired men (N = 180). The weakest support was found for 151 perceived susceptibility and perceived severity. Participants who had high scores for general perceived barriers, perceived barriers to vaccination, no perceived general benefits, no perceived specific benefits, and no general benefits were more likely to report being unvaccinated. The findings demonstrated that perceived barriers and perceived benefits were the dominant predictors to the outcome variable. These studies mentioned above supports the finding of this study with regard to perceived benefits as significant predictor to the intent to be screened for prostate cancer. Nonetheless, the data for this study did not find any significant statistical support for the other two predictor variables examined by this study. Hypothesis 1 proposed that there would a predictive relationship between the three predictors (perceived susceptibility, perceived benefits, and perceived barriers) and the outcome variables (intent to be screened for prostate cancer). Hypothesis 2 projected that perceived susceptibility would be statistically the most significant positive predictor to the intention 152 of Haitian men in Haiti to screen for prostate cancer. The data analysis did not find enough evidence to support perceived susceptibility as a relevant predictor of intent to be screened for prostate cancer among this sample. This clearly indicated that perceived susceptibility was not a strong contender as predictor. Only beliefs about barriers were found to be a significant predictor of exercise ( =-. Through 363 valid surveys, they found that perceived benefits and perceived barriers were proximate determinants of condom use (r = 0. Nevertheless, several studies also support perceived susceptibility as a strong predictor of health behavior. Kleier (2010) surveyed 143 Haitian-American men to (a) 153 look at if perceived susceptibility to prostate cancer was compatible with the objectively measured disease risk, (b) check the relationship of perceived susceptibility and fear, and (c) examine these constructs for their predictive relationships to screening behavior. Although it has been mostly in combination with other constructs, perceived susceptibility is usually noted as a strong predictor (Abuadas et al. The model recognized that notion of perceived threat as the combination of perceived susceptibility and perceived severity (Champion & Skinner, 2008; University of Twente, n. Through a series of revisions and testing, the combined constructs, perceived susceptibility and perceived severity, were found to be the determinant of perceived threat (see Figure 4) (Becker & Janz, 1985). Perceived threat is considered the most predictive construct with regard to health-related behavior (Champion & Skinner, 2008). By means of several revisions, Champion found that the construct, perceived severity, has very little variance with perceived susceptibility. It was then determined that perceived threat could be measured by examining perceived susceptibility alone (Champion, 1999). This hypothesis originally suggested that there would be a statistically significant positive relationship between Haitian men of different ages and their intent to screen for prostate cancer. As the data for the outcome variable was 154 changed from continuous to categorical data, the hypothesis was reconfigured to consider if the likelihood of being screened for prostate cancer was predicted by the participantsage. The data were analyzed through a binary 2 logistic regression, and results indicated that the model to be not significant, (1) = 3.
The etiologic and the fetuses are decomposed skin wounds become contamiagents are protozoan parasites or mummifed anxiety 36 weeks pregnant trusted 5 mg buspirone. The most the organism is sensitive to does that recently have delivered effective prevention of losses is some antibiotics physical anxiety symptoms 24 7 order buspirone mastercard, including young are most susceptible anxiety symptoms one side of body generic buspirone 10 mg line. The frst this organism is known espesigns are listlessness anxiety prayer generic buspirone 5 mg with mastercard, ruffed hair cially for causing infection in coat, loss of appetite, and the mammary glands of nursing diarrhea. The breasts become swolrate increases, and body temperlen, hot, and may become bluature may rise. Small, white nodnella infections are uncommon changes are present in the intesules also may be found in the in domestic rabbits. The lungs infected animal can quickly lymph nodes may be soft, hemare consolidated, with numerinfect a whole colony. The bronalso can become infected by rabbits become carriers and may chi and trachea may contain a human caretakers, as Salmonella shed bacteria in their feces intermucopurulent exudate. Bacteria enter the skin Salmonellosis in rabbits genStreptomycin and other antithrough broken or abraded areas erally is caused by Salmonella biotics have been used effectively following birth; transmission typhimurium or S. All members of the respond to the medication, but passages of rabbits, and the close salmonellae group are aerobic, may continue to excrete 1 Archival Copy. Occasionally, small, eye with sterile saline or boric for both direct contact and aerosuperfcial pustules or abscesses acid solution, and applying an sol transmission. The doe enter the body through abrasions this condition sometimes is allemay refuse to nurse her young or scratch wounds that become viated by intravenous antibiotic and generally loses her appetite. Consult a veterinarian for on the lower eyelid near the the doe or when the young are current recommendations. Mastitis the septicemic form of staphTreponematosis Mastitis most commonly ylococcosis results in peracute is caused by Staphylococcus (vent disease) death in young rabbits, primarily aureus; it is discussed under Treponematosis, sometimes those still in the nest box. After fnding that eyes with a copious exudate are rabbits had a natural spirocharacteristic of this disease. The There is a great deal of confubacteria most often isolated are sion concerning the incidence of Staphylococcus aureus and Pasteu treponematosis in rabbits. Conjunctivitis Recent reports indicate it is is treated by opening the eyeFigure 8. In fact, serological tests Spirochetes also are found in with pathogenic bacteria and have demonstrated antibodies to regional lymph nodes, and becomes very sore. Injections are given at seems to thrive in flthy condiprimarily by breeding, and an weekly intervals, and all rabbits tions, enters the host through isolated case can lead to an outmust be treated, regardless of the contaminated food or water. The lesions are to differentiate the two diseases sanitation procedures, including irregular in shape, tan brown, without the use of a dark feld disinfecting cages, nest boxes, and either edematous or dry microscope. Sometimes weeping, scope, the spirochetes of trepodisease has been diagnosed in coalescing vesicles are found. It is Transmission of the disease an important malady of wild by mosquitoes led to the name rabbits, but not of domestic mosquito disease. Screen enclosure eral weeks; the disease is fatal matosis exhibit no characteristic of the entire rabbitry is an effeconly in the very young. Antibitrast, the disease can completely the infection can be diagnosed otics are not effective in treating wipe out some susceptible popudefnitely. The cut survaccine is not approved for use tribution of the California brush face of each edematous subcutain the United States. The virus neys, liver, intestinal tract, bone the lesions include lymphadenican be recovered from lesions on marrow, and mesentery. Given the proper envirabbits in southern California, virus rarely is a cause of epizootronment (such as an epizootic in but the virus produces no eviics, but usually is very serious wild cottontail rabbits) and an dence of a generalized illness. Vaccination adequate mosquito population, the most common sites for with vaccinia virus confers this viral disease could result papillomas are the ears and eyeimmunity. The lower portions of the isolated from nodules beneath uli of rabbits exists as a latent growth are pinkish and feshy to the skin of wild cottontail rabinfection in some stock lines of the touch. The virus does older, they increase in size, growths) were transmitted to not produce a natural disease, become more cornifed, and are domestic rabbits. A virus with charthey are easily scratched off by infected only wild cottontail rabacteristics of the herpes group the rabbit or knocked off when bits; however, an outbreak has has been recovered from rabbits handled. Oral papilloma Wartlike growths in the mouth, especially on the lower surface of the tongue, are caused by a virus (one of the papovaviruses) different from the rabbit papilloma virus. The the body organs such as the Viral hemorrhagic clinical signs and pathology of lungs, liver, heart, spleen, and disease the viral enteric diseases are very mucous membranes. Rabinvaders) or whether natural outvigilant eye on imported rabbits bits with the disease show incobreaks of enteritis can be caused and rabbit meat. There great deal of work currently is in Australia and New Zealand usually is a bloody nasal disbeing done to answer the quesand is decimating wild Oryctolcharge. Fungal infections must be diffi ferentiated from other types of skin problems, such as mite infestations, hair pulling, fght wounds, molting, and vitamin defciencies. The best preventive ligrams (mg) per pound of free from the infective forms measures are sanitation, good body weight per day for at least of parasites. Parasitic diseases Rabbits are susceptible to a number of parasites, but only a few are of economic importance. To Ear mites adult and potential replacement treat fur mites in a few rabbits, Psoroptes cuniculi, the comrabbits in the herd. Massaging apply a cat fea powder at weekly mon ear mite of rabbits, causes the base of the ear after adminisintervals for several treatments. This conditering the medication distributes If a fur mite infestation becomes tion is a very common parasitic the drug throughout the sura herd problem, treat with injecdisease in commercial rabbitries. This dark cotton tipped applicators and Larvae of Cuterebra fies are encrustation consists of cellular tweezers before drug application. In able ear mites monthly for three worms hatch from these eggs severe cases, the entire inner treatments. Ivermectin is given and burrow into the skin to form surface of the pinna may be two or three times at 2 week warbles. The warbles cause Treatment of ear mite infestarabbits these mites seldom cause tions requires a plan and persea problem and rarely are noticed. Diagnosis of fur mites is best Most mineral oil based ear accomplished by scraping the mite medications containing a skin of the affected area with a Figure 13. Paint the wound with To destroy adult feas, dust rabof the reservoirs of tularemia, an antiseptic. Control immawhich domestic rabbits are being infested with feas; however, the ture forms by burning old raised. In these locations, the parasite multiplies extensively and then sheds eggs in the feces. Not all species of coccidia are equally harmful, and rabbits tolerate moderate numbers of some without displaying illness. In some cases, patches of epithelium die and slough away from the intestinal wall. Control of intestinal coccidiosis depends largely on management practices that minimize the danger of fecal contamination of feed, water, and hutch foors. Design feeders so that controlled more easily by proper breakdown of antimicrobial resifecal contamination is held to a management. Infections lasting more Oocytes persist in the environEncephalitozoon cuniculi (a than 16 days can be recognized ment and are diffcult to kill protozoan parasite) is the cause by white circular nodules on the with most common sanitizing of a mild but long standing disliver (Figure 15). When indicated, a nephritis caused by the parasite there are no unusual sympration containing 0. The histologically, but grossly the mon protozoal disease of rabbits organisms are passed in the urine organs may be swollen, and caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis There are two forms of the Diagnosis of encephalitogenerally is accomplished at disease. In the acute form, the zoonosis in a rabbit herd is necropsy by observation of hisrabbit develops anorexia, fever, diffcult. Recently, several diagmost cases is not practical, and sis to generalized convulsions. These tests may be helpful taminated with toxoplasma form, either no symptoms are in antemortem diagnosis and oocysts.
