Dilantin
Mark J. Spoonamore, MD
- Assistant Professor, Clinical Orthopedic
- Surgery
- Medical Director, Center for Spinal Surgery,
- University of Southern California? Keck School of
- Medicine, CA, USA
In the placenta symptoms 4 days post ovulation buy 100mg dilantin free shipping, hemozoin can only be found slightly which is produced from hemoglobin catabolism within Plasmodium infected erythrocytes symptoms hepatitis c purchase dilantin online from canada. Its presence is an indication of placental infection and it is associated with decreased foetal weight (Rogerson et al medications listed alphabetically purchase dilantin overnight. Histological pic tures of the active form of placental infection show black/gray colour treatment stye 100mg dilantin with visa, dense sinusoid with infected erythrocytes medications diabetic neuropathy purchase dilantin on line amex. Syncytial knots can occur with fibrinoid necrosis and thickening of the basal membrane and damage of trophoblasts (Suparman medicine daughter lyrics cheap dilantin 100mg mastercard, 2005). In conclusion, malaria infection in pregnancy can cause severe anemia and low birth weight and increases the risk of death (Khong et al. Malaria during pregnancy in reference center from Brazilian Amazon: Unexpected increase of the frequency of Plasmodium falciparum Infections. Acute atherosis in pregnancies complicated by hypertension, small for gestational age infants, and diabetes mellitus, Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine,115(7):722-725. Effects of malaria during pregnancy on infant mortality in an area of low malaria transmission. Localization of hyaluronan with a hyaluronan-specific hyaluronic acid binding protein in the placenta in pre-eclampsia. Maternal-Child Health Interdiscplinary Aspects Within the Perspective of Global Health 227 Mc. Molecular mechanisms of Plasmodium falciparum infection in pregnancy-associated malaria in Timika, Papua, Indonesia. Placental monocyte infiltrates in response to Plasmodium falciparum infection and their association with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Switches in expression of Plasmodium falciparum var gene correlate with changes in antigenic and chytoadherent phenotypes of infected erythrocytes. Lack of an association between antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum malaria-associated glycosylphosphatidylinositols and placental changes in Cameroonian women with preterm and full-term deliveries. Those cases were mostly tourists who had visited endemic countries or migrants who were diagnosed and treated in the United States (1, 2, 3). Transfusion-transmitted malaria is one of the incidents of infections transmit ted by blood transfusion from the donor to the recipient. It has serious conse quences for the patient as in many countries diagnosis is rarely considered in the recipients of a blood transfusion (4, 5). These results indicate that the majority of blood which is used for trans fusions in these areas contains antigens of either Plasmodium falciparum or P. The question is whether or not a potential donor has visited or lived in a malaria endemic area or not. Within this context both the length of the time the donor stayed in a malarious area and the length of time since he has visited a malarious area are very important factors and need to be taken into account when trying to identify any potential risk for transfusion-transmitted malaria. Malaria that is transmitted by transfusion from the donor to the recipient manifests with a shorter incubation period of 2-4 days since the inoculum contains already the erythrocytic parasite stages (trophozoites and merozoites) and therefore a pre-erthrocytic liver cycle of the parasite is not necessary. In fact, diagnosis of transfusion malaria requires a keen sense of clinical sus picion. In case of any blood transfusion, and if the recipient develops some of these symptoms, he should definitely be tested for malaria. After infection, individuals can remain infective for weeks to months, or even years, in the case of P. Therefore, those who have suffered from malaria cannot donate blood for at least 3 years after becoming asymptomatic, and proven carrier P. State of malaria diagnostic testing at clinical laboratories in the United States, 2010: a nationwide survey. A simple and fast method to exclude high Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia in travelers with imported malaria. Plasmodial antigen detection by monoclonal antibody as a screening procedure for blood donors in transfusion medicine. Screening malaria at blood transfusion in red cross unit, banjar district, south Kalimantan province. Seed C, Cheng A, Keller A: Comparison of the efficacy of two malarial antibody enzyme immunoassays for targeted blood donor screening. Maternal-Child Health Interdiscplinary Aspects Within the Perspective of Global Health 233 13. The causative organisms are shed in the urine of affected animals and humans into the environment. Leptospirosis is pre sumed to be the most widespread zoonosis in the world (Hickey and Deemeks, 2003). In the tropical and sub-tropical areas, the seroprevalence of antibodies to leptospira may vary from 20 to 30% among subjects tested serologically (Gasem, 2005). Humans get infected by direct contact with the infected animals or indirect by contaminated water with urine of infected animals. The organism is invading the body through skin wounds or mucous membranes (gastrointestinal and respira tory tract) and conjunctiva (Faine, 1982). Rats, pet animals (dog and cat) and live 236 Bambang Pontjo Priosoeryanto and Risa Tiuria stock (cattle and pig) were reported serologically positive for leptospira in Indone sia. The true incidence is not precisely known due to the fact that the disease is of ten overlooked or misdiagnosed and therefore under-reported in most endemic areas. Leptospirosis may be under-diagnosed because the diagnosis is difficult to confirm, it may be confused with other diseases, and the disease may be mild and not be investigated in the laboratory. On the other hand, laboratory facilities to perform standard diagnostic tests for leptospirosis are rarely available in endemic areas (Gasem, 2005). The clinical signs of leptospirosis vary from fever, icterus, haemoglobinuria and abortion in pregnant animals. The severity of this disease depends on the serovar of Leptospira, the species of infected animal and the geographical area (Ebrahimi et al. During the last decade, leptospirosis outbreaks have been reported in many countries such as Indonesia, India and Malaysia. In Indonesia, in 2007, not less than 20 provinces were positive for the disease (Jakarta; Banten; West, Central and East Java; Yogyakarta; Lampung; South, West, and North Su matera; Bengkulu; Riau; West and North Sumatera; Bali; West Nusa Tenggara; North and South Sulawesi; West and East Kalimantan) but in 2012, 33 provinces were reported positive. Transmission occured when animals contract the disease by eating and drink ing Leptospira-contaminated water, or by direct contact of broken skin or mucous membranes with mud, vegetation or aborted foetuses of infected or carrier ani mals. Recovered animals and animals with unapparent (subclinical) leptospirosis frequently excrete billions of leptospiras in their urine for several months or years. Partoatmojo (1964) re ported and stated that since 1936 several serovars have been isolated from domes tic and wild animals. Orr and Darodjat (1978) on their study in West, Central, East Java and Bali provinces reported cases of leptospirosis in cattle and pigs with more than 6 serovars of Leptospira. Sumariyanto (1981) also detected 3 serovars of Leptopsira Maternal-Child Health Interdiscplinary Aspects Within the Perspective of Global Health 237 from rats in Bali. In Medan of North Sumatera, Gani and Setyowati (1990) report ed a case of leptospirosis in rats from pig farming. The average number of leptospirosis which was found in the study of Kusmiyati et al. From this figure we can see that these animals could act as a reservoir in the environment and also as a source of infec tion to other animals as well as to humans. Figure 1: the average number of animals and humans in Indonesia with an im mune response against Leptospira, collected and adapted from several reports (Kusmiyati et al. In dairy cattle, fever and decreasing of milk production are common in infected animals; while reproduction disorders are found in pigs. In dogs, clinical signs of canine leptospirosis depend on the age and immunity of the host, environmental factors affecting the bacteria, and the viru lence of the infecting serovar. The signs are fever, vomiting and jaundice while sub-clinical manifestation 238 Bambang Pontjo Priosoeryanto and Risa Tiuria is also commonly found. Leptospira interrogans serovar pomona in cattle causes fever, depression, acute anemia, haemorrhages and red water; while serovar hardjo in pregnant or lactating cows causes fever, decreasing milk production and abortion. In dogs, four types of Leptospira infection have been found: 1) peracute infec tion, this type can be associated with massive leptospiremia and death which may occur rapidly with a few premonitory signs. The serovar hardjo was isolated by Wolf in 1938 from a rubber farmer in Deli of North Sumatera. In the early 1970s, human leptospirosis was reported by Fresh in South Sumatera and Bangka Island as well as in several hospitals in Jakar ta. The outbreak of human leptospirosis at the transmigration area of Kuala Cina Maternal-Child Health Interdiscplinary Aspects Within the Perspective of Global Health 239 ku in the Riau Province of Sumatera was reported by Simanjuntak et al (1986), pointing out that leptospirosis in humans was mostly transmitted by rats. Leptospirosis is usually found in the rice farmer as well as in plantation, mining, slaughter house and military personnel. In people who are older than 50 years, the fatality rate can reach 56%, in patients with hepatic leptospirosis and icterus the fatality rate could be higher. The risk factors associated with human leptospirosis vary and they are mostly related to the exposure of humans to infected animals. The origin of infection in humans is usually a direct or indirect contact through urine or other body fluids of infected animals such as wild or feral animals, domestic pets or livestock. The or ganism can enter the body through skin wounds, intact skin or mucous membrane (gastrointestinal and respiratory tract) and conjunctiva. Leptospiral infection in human may be acquired via occupational or recreational activities. In wet tropical areas, where many rodents or farm animals live, human leptospiral infection is not limited to an occupation but more often to environmental contamination. Envi ronmental factors that are associated with the transmission of leptospirosis are high population of rats, presence of dogs around the home, bad flow in gutters of the housing, and stagnant water. Outbreaks of leptospirosis are associated with water and animals in the context of swimming, drinking contaminated water or living in flood-prone areas etc. In the same period 142 specimen of rodents serum 47% were positive to 4 serovar of Leptospira (pyrogenes, bataviae, icterohaemor rhagiae and canicola). In March 2004 in the city of Makassar in South Sulawesi 7 patients were positive to Leptopsira of whom 5 people died. In 2011 the cases increased especially in Jogya karta when an outbreak of leptospirosis has occurred as seen in Figure 3; and also in one hospital in West Java up to January 2012 (unpublished data) 23 cases were recorded. In 2012, cases still occurred in Jogyakarta though the number went down in March 2012 Figure 3. Yearly cases of human leptospirosis in Indonesia from 2004 March 2012 (Aditama, National Coordination Meeting on Zoonoses, Ministry of Health, 2011). Year 2012 data only from Jogyakarta (Anonymous, 2012) 4 Leptospirosis in mothers and children In human mothers, leptospirosis is extremely dangerous in all trimesters of preg nancy for both the mother and her foetus there is a risk and also a potential issue for breast-feeding mothers. The foetus can be infected across the placenta due to the bacteria that could pass the barrier. This ?transplacental infection means that the foetus can become ill, independent of the mother who may have such mild Maternal-Child Health Interdiscplinary Aspects Within the Perspective of Global Health 241 symptoms that she does not notice any illness herself. Infection through transplacental transmission is very common where the mother is infected, and the outcome varies depending on the timing. The infected foetus will develop the same clinical symptoms as an adult so it can suffer from jaundice, renal damage, vasculitis and haemorrhages especially in the first and se cond trimester where the foetal immunity response is absent. If the foetus is in fected in the third trimester it can often present an immune response, and if it survives it will usually continue to develop and be born without abnormality. Several studies from Vietnam, and Cambodia on the seroprevalence and the clinical signs of the disease including mild disease in children have been done (Thai et al. In India, based on the report of Tullu and Karande (2009), the disease has been endemic in the Indian states of Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Andamans. Also, with improvement in diagnostic facilities over the past few years, leptospirosis is being reported from almost all the cities and states of India, including Delhi, Mumbai, Uttar Pradesh, Orissa, and Gujarat. Thirty out of 93 (32%) urban slum children from Mumbai admitted for suspected leptospirosis. In one case in a hospital in Central Java-Indonesia (unpublished data) the pregnant mother with her baby died during delivery and both were positive to leptospirosis. The figure of maternal-child leptospirosis infections in Indonesia seems to be bigger than it is, since Indonesia has only two seasons, the dry and the wet (rainy) season and it mostly occurs during the flooding in the rainy season when the contact of people/animals with rat urine-contaminated water is most frequent. The same figures seem to occur in developing countries that lack infra structure, medical aid and where poor environmental conditions exist. In devel oped countries young children are less susceptible to infection than adults as the general population has no innate immunity to the infection and there is no vaccina tion program. The issues, when dealing with young patients, are those of commu nication and medication. Young children are often exposed to leptospira because of their playing and sports activities swimming in rivers, lakes, fishing, or throughout floodings and when touching infected animals. The spreading and out break of leptospirosis is most likely caused through contaminated water. For preventing and control of lepto spirosis in animals and humans, good collaboration and integration activities of veterinarian and medical doctors in all medical aspects are absolutely needed and improved education and socialization of the high-risk population is a must. Leptospirosis infections might be prevented by avoiding or minimizing poten tial risk factors. Measures that might be useful to prevent leptospiral infections are : 1) drainage of contaminated waters, 2) improving quality of living environment including education, 3) water management (flood-prone area, farming etc. Murine typus and leptospirosis as causes of acute undifferentiated fever, Indonesia Dispatch, 15(6). Penyelidikan mengenai leptospirosis: Penyakit zoonotik yang berarti bagi ekonomi dan kesehatan masyarakat di Indonesia. Survei serologik terhadap brucellosis dan leptospirosis pada ternak potong di Jawa Tenga, Jawa Timur dan Bali. Retrospective immunohistochemical detection of leptospirosis in dogs with renal pathology.
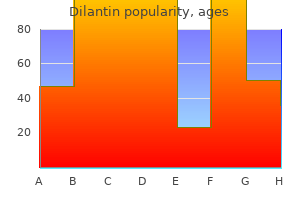
The vaccine provides the greatest benefit for those aged 70?79 because the incidence of shingles and the risk of developing complications is higher for those aged over 70 medications names 100mg dilantin mastercard. The shingles vaccine reduces the likelihood of shingles and of post herpetic neuralgia medications similar to gabapentin best 100mg dilantin. Shingles can still occur in vaccinated people medicine images order 100mg dilantin otc, but the severity of symptoms is likely to be milder and symptoms will have a shorter duration medications dispensed in original container buy 100mg dilantin with visa. While the vaccinations have been recorded in the Australian Immunisation Register since late 2016 treatment jalapeno skin burn buy dilantin on line, data on vaccination coverage for shingles have not yet been reported symptoms 4 dpo discount 100mg dilantin otc. Stronger evidence, better decisions, improved health and welfare Shingles notifications Since 2006, varicella-zoster (which causes chickenpox and shingles) has been notifiable in all Australian states and territories apart from in New South Wales. This means that diagnosed cases are reported to state or territory health departments. However, in many cases the notification does not specify whether the person has chickenpox or shingles. Furthermore, each year many shingles cases do not seek medical care or do not have formal laboratory tests done, so their illness is not reported. For these reasons, notifications are likely to be an underestimate of the true number of shingles cases occurring in Australia. Hospitalisations and deaths due to shingles In 2016, there were 2,677 hospital admissions for shingles in Australia. The rate of admissions increases as age increases, and is highest among people aged 80 years and over (left figure). Between 1997 and 2016, shingles caused 438 deaths, 83% (365 deaths) of which occurred in people aged 80 years and over. Identify typical signs and symptoms of viral diseases spread by airborne transmission 3. Identify typical signs and symptoms of common food borne and waterborne viral diseases 3. In the present article, we wanted India to discuss about the causative agents/organism, mode of infection, symptoms, treatment, vaccination, available molecular biological techniques and public awareness regarding this Siddhartha Maity Department of Pharmaceutical infection. These groups of infections are the main threats of serious congenital infection during pregnancy, which may ultimately cause fetal damage or other anomalies. In most cases, the infection can be severe enough to cause serious damage to a fetus than his/her mother. The placenta forms a barrier between mother and fetus during the first trimester of pregnancy that protects the fetus from the humoral and cell mediated immunological response. Although, the fetus gets immunity from mother, they are seriously infected by these viruses due to lack of immunity after the first trimester of pregnancy. All the infections have their own causative agent and generally they spread through poor hygienic conditions, contaminated blood, water and soil and airborne respiratory droplet. It will be dangerous, if a fetus show microcephaly, intracranial calcifications, rash, intrauterine growth restriction, jaundice, 2 hepatosplenomegaly, elevated transaminase concentrations and thrombocytopenia. Correspondence: Some specific symptoms of these infections are tabulated in Table 1. Sudipta Saha Department of Pharmaceutical techniques have been discussed for detection of this disease in Table 2. The common Sciences, Babasaheb Bhimrao cause of contamination of this disease has also been described in Figure 1. In the Ambedkar University, Vidya present article, we wanted to discuss about the causative agents/organism, mode of Vihar, Rai Bareli Road, Lucknow infection, symptoms, treatment, vaccination, available molecular biological techniques 226025, India Tel: +91-8090747008 and public awareness regarding this infection. Causative organism: Toxoplasmosis is usually a benign 3 Treatment: After early detection, the mother can be anthropozoonosis, caused by Toxoplasma gondii (T. The parasites cross recommended along with supplements of folinic acid to the placenta and infect infants. Congenital toxoplasmosis is prevent the bone marrow suppression caused by usually not apparent at birth and about 70-90% of infants 1 pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. The classic triad Others Infections hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, and intracranial 3 Syphilis Infections calcifications reported very rare. Causative organism: It is caused by gram negative 2 spirochete Treponema pallidum (T. It has Diagnosis: When a woman has infected with a pathogen 1 100% vertical transmission ratings. Syphilis affects pregnant women in three while IgG antibodies remain detectable for a lifetime, stages: providing immunity and preventing or reducing the severity of reinfection. Thus, if IgM antibodies are (a) Primary stage appearance of the syphilitic chancre present in a pregnant woman, a current or recent and lymphadenitis. The causative organism can be isolated from placenta, serum, and (b) Secondary stage rash on the hands and feet even after 2 2-10 weeks of chancre heals. Diagnostic testing for the causative organism in the fetus, whose mother has evidence of acute (c) Tertiary stage neurological, cardiovascular, and infection, can be performed more precisely as early as gummatous lesions (granuloma of the skin and within 18 weeks of gestation using polymerase chain musculoskeletal system). Elevation of protein level and pleocytosis can be seen in Symptoms: Early manifestation could be hemorrhagic 2 nasal discharge (?sniffles), hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice, the cerebro-spinal fluid during toxoplasmosis. Rising increased liver enzymes, lymphadenopathy, hemolytic 260 Journal of Scientific and Innovative Research anemia, thrombocytopenia, osteochondritis and periostitis, Causative organism: It is a member of the herpes virus mucocutanous rash, central nervous system abnormalities, family. A newly infected person is (small teeth with an abnormal central groove), mulberry contagious from 1 to 2 days before the onset of rash. The molars (bulbous protrusions on the molar teeth resembling average incubation period for varicella is 14 to 16 days mulberries), hard palate perforation, eighth nerve deafness, (range 10?21 days). After the primary infection resolves, interstitial keratitis, bony lesion, and saber shins (due to the virus enters the latent phase and remains dormant in the 2 chronic periosteitis). Reactivation may occur along the 8 sensory dermatome to cause herpes zoster, or ?shingles. Diagnosis: Diagnosis of syphilis can be performed using dark-field microscopy or detected using direct immune Symptoms: Herpes zoster during pregnancy has been 3 fluorescence assay of the collected sample taken from observed very rarely (one cases in 200000 pregnancies). A presumptive diagnosis is Only 2% of fetuses whose mother have infected with this made using nontreponemal and treponemal tests. Non virus in first 20 weeks of pregnancy will develop varicella 1 treponemal tests included the venereal disease research zoster virus embryopathy. Treponemal tests should not consider alone hydrocephalus, microphthalmia, duodenal stenosis, jejuna when false positive results have been shown by some other dilatation, microcolon, atresia of the sigmoid colon, infections such as Lyme disease, yaws, pinta, and cicatricial lesions of skin/hypoplasia of tissues in a leptospirosis. Sometimes a false negative result may also dermatomal distribution, cataracts, chorioretinitis, seizures, be seen due to excessive antibodies known as ?Prozone 2 hypotonia, hypo-reflexia, encephalomyelitis, dorsal effect. Proper treatment Treatment: In case of severe maternal infection, antiviral of the mother leads to eliminate the risk of infection of agent acyclovir can be used for treatment. Mode of infection: Most infants are infected through Varicella-zoster virus Infection contaminated blood or body fluids during delivery. It replicates in 261 Journal of Scientific and Innovative Research hepatocytes and interferes with hepatic functions. In order Causative organism: Rubella or German measles is a to counter attack the virus, the cytotoxic T cell is activated member of Togaviridae family. Its 1 at the time of acute infection increases, risk of chronic incubation period is about 2-3 weeks and is contagious. It causes Erythema infectiosum (slapped haemorrhagic manifestations, neuritis, orchitis etc. Infection of a negative mother occurs calcifications, branch pulmonary artery stenosis, patent due to contact with children having Erythema infectiosum ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defects, coarctation of infection. If Mother is serologically positive for specific B19 Health education: Vaccination is the best way of the antibodies are prone to infection. Ultrasound technique can prevention of infection in the women 28 days before also be performed to detect the development of fetal conception. Those women who are non-immune to rubella should Treatment: however, there is no specific treatment for 6 avoid the infected person. Postnatal infection can be spread family, most common congenital infection in United through infected persons kissing or touching the infant. Symptoms: About half of the women having primary Mode of infection: It is transmitted to an infant during infection are asymptomatic. About 20% mothers show pregnancy, ingestion of infected human milk, direct symptoms like vulvovaginitis and cervicitis. It is easily spread in day of cases present with characteristic vesicular and ulcerated care centers and family having many young children. Infants show complications like to endogenous reactivation of virus, it can cause severe (a) Skin lesions: vesicles, vesiculobullous, ulcer, pustular, illness in the transplant recipient immunosuppressed 2 erythematous, and scarring. Infants showed various complications such as optic atropy, (c) Eye lesions: keratoconjunctivitis, chorioretinitis, microcephaly, hypotonia, intracranial calcifications, and 6 cataracts, retinal detachment. If the mother has a primary infection during Diagnosis: Diagnosis can be carried out by taking the 6 pregnancy, fetal morbidity rate is high. Skin, eye and mouth infection can birth, it will be very difficult to differentiate between be easily detected in 24-36 hours by viral culture. Adequate hydration also requires seizure ranged from 10 to 56% in children with minimizing kidney complications. This assay method permits many different analysts have promising effect to control the infection. People tend to spend their limited mental reserves on resources that they lack, and so hungry children focus on food, which can lead to neglect of other areas of life such as schoolwork. Families often work to keep their food insecurity hidden, and children may feel stigmatized when using free and reduced lunch programs and other social services. If properly funded and implemented, our nutrition assistance infrastructure can mitigate hunger and food insecurity, enabling children to reach their full potential. Preventing Chronic Disease: Public Health Research, Practice, and Policy, 10, E34. The impact of the National School Lunch Program on child health: A nonparametric bounds analysis. Opinions and statements included in the paper are solely those of the individual author, and are not necessarily adopted or endorsed or verified as accurate by the Committee on National Statistics and Food and Nutrition Board or the National Academy of Sciences, including the National Academy of Engineering, Institute of Medicine, or National Research Council. Introduction and Background the current officially recognized measures of food security, food insecurity and hunger for the U. The conceptual framework and measurement approach used to develop the measures were built on a foundation of federal interagency activity with input from research conducted by public and private institutions. Results of scale development by the Food Security Measurement Project team were published in three reports 2,3,4 released in 1997. Substantive revisions improved the validity, reliability and overall effectiveness of the measures. Further examination of data from the Child Food Security Scale also revealed important differences between child hunger results obtained by scoring and scaling data from the full eighteen-item scale compared to those obtained when data from the Child Food Security Scale was used 7 separately. Estimating child hunger prevalence (later referred to as very low food security in children) using data from the eighteen-item scale resulted in underestimation of its prevalence, particularly among households with children of broadly different ages. They were intended and developed to serve nutrition monitoring and research needs of the academic/scientific community (both public and private), state and federal government agencies, and the U. Considered in light of the three conceptual domains described above, this property suggests logical points on the scale (indicated by specific questions), at which the severity of household food security changes. A shortcoming arising when the child-referenced items were separated from the adult referenced items and re-scaled as a separate scale is that there are no questions in the child scale asking about the affective (worry, anxiety) component of food security. Thus, while households with children in which the respondent affirms 0-1 item only are typically considered to have high 4 (0 items affirmed) or marginal (1 item affirmed) food security among children, if the respondent affirms 0 items, it is not possible to rule-out the presence of this affective component. Table 1: Child Food Security Scale questions with thresholds and categories Food Survey Security * Question Question Content Category Raw ** score 0-1; High or ?We relied on only a few kinds of low-cost food to feed our children marginal because we were running out of money to buy food. Raw score = 1 may be considered marginal food security among children, but it is not certain that all households with raw score zero have high food security among children, because the scale does not include an assessment of the anxiety component of food insecurity. This person has been referred to as the ?household food manager, and is often the mother (or primary female caregiver) in households with children. When children are present the adult respondent provides information about all children as a group, not individual children. Likewise, the adult respondent provides information for all adults in the household as a group, not individual adults. Several review articles have been published that summarize food security research related 12,13,14 to child and adult health in the U. What We Have Learned About Food Security and Health in Children Research on relationships of food security to health, in children and adults, indicates that food insecurity is associated with a variety of adverse physical and mental health outcomes, and that food insecurity influences health through two primary kinds of pathways; nutrition pathways 14,13,12 and non-nutrition pathways. Of special interest are nutrition pathways that influence brain and cognitive development during the first 3 years of life, including the prenatal period. Throughout this early developmental period, neurotransmitters are also synthesized from nutrients, playing initial important roles in organization of cell differentiation and specialization, and later assuming their primary function in neuro-transmission. The developmental processes occurring during the prenatal period accelerate and continue after birth, and are especially active and creative during the first 3 years of life (Figure 1). Figure 1: Timing of Synapse and Neural Network Formation in Humans by Primary Function Food insecurity can make it extremely difficult, or impossible, for pregnant mothers to maintain the quality of their own diet and nutrition, and to provide consistently good nutritional 24 materials for their babies growth and development. Mothers decisions to breastfeed or not have major consequences for their babies food and nutrient needs. If a mother breastfeeds her baby, her food and nutrient needs take on particular importance in support of lactation and nursing. The myelin sheath that encapsulates the axon of each neuron is critical to effectiveness of signal transmission along the axon. Synapses are the neurobiological substrate for almost all nerve cell to nerve cell communication. Synaptogenesis, the development of synapses, is also vulnerable to malnutrition 10 and exposure to environmental toxins. Synapses develop at different times in different parts of the brain, with the process of synaptogenesis continuing into adolescence in humans, lengthening 22,23 the time period of vulnerability of this very important developmental process. Learning Optimally, human infants and toddlers are well prepared for learning, which will be an important activity for their entire lives.
Morphine causes his ?Coanalgesics tamine release symptoms shingles safe dilantin 100mg, which may cause vasodilatation medicine examples dilantin 100 mg with mastercard, but it is Drugs such as antidepressants and anticonvulsants are usually mild and bene? Intravenous steroids such as dexa prefer to see a patient struggling and showing signs of methasone are becoming more popular for use as anti life rather than pain free and sleeping quietly treatment 5th metatarsal shaft fracture dilantin 100 mg without prescription. Some tie emetics after surgery treatment 101 purchase dilantin paypal, but they have not been proven to up such patients to their beds when they are struggling medications are administered to order 100 mg dilantin fast delivery. Others resort to sedatives and hypnotics symptoms 14 days after iui quality dilantin 100 mg, such as diaz epam or even chlorpromazine. Many patients are rest Nonpharmacological methods less because they have pain or a full bladder. Tese methods should be Is the pain threshold higher in used more whenever possible. They may, therefore, request more drugs cated about acute pain and its management in the and will be able to tolerate them better. Consent is not normally re ever, no respecter of race or class, and every individ quired except for experimental and research pur ual must be treated as unique. Intravenous, rectal, or oral routes can be used in an upward or How to organize pain management downward stepladder manner depending on the after major surgery circumstances. Pain relief may require the barest mini an important role in any acute pain service and mum of sta? Such equipment, and good monitoring are essential in guidelines help countries, especially those with the least all institutions where major surgery is done. Optimum monitoring of the patient should in ward rounds, run emergency services for com clude equipment for respiratory monitoring, in plications, carry out research, and conduct audits cluding pulse oximetry and cardiovascular moni on pain management. Simple sedation ob service with guidelines and protocols to cover servation charts and early warning charts for ad children and adults in accident and emergency verse events will help manage even the most dif wards, operating rooms, and recovery wards as? Relying on the cases because systemic analgesic drugs may mask symp sympathetic responses caused by pain to arti? Local and re especially in high-risk patients after major sur gional anesthetic blocks are grossly underused. Deep vein thrombosis, bleeding, and other hema ingly used for continuous, patient-controlled, or tological problems a? Women may seem to tolerate pain better than ability of these pumps should improve sooner or men, but this is not a general rule. However, if doses are severe pain, pyloric and bowel surgery with moderate titrated carefully to the desired e? Intrathecal and epidural local anesthetics with and some valve repairs and closure of congenital mal opioids are commonly used. Ac severe pain, craniotomy and resection of brain tumors etaminophen and dipyrine, if they are not contraindi with moderate pain, trauma and skull fractures with cated, will help with the pain and the pyrexia seen in moderate pain) septic patients. Large doses of opioids can cause hypoventilation and increase intracranial pressure. International and national drug regulatory bodies problems and should be planned and practiced in partnership with governments and local sup with clear written guidelines and protocols. Public perceptions of postoperative pain and its should be made to provide enough funds to im relief. Drug policies and control, including essential drugs list Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings Chapter 15 Acute Trauma and Preoperative Pain O. Aisuodionoe-Shadrach When acute trauma occurs, the diagnosis and purposeful ries that may pose a potential danger to life besides the management of pain should be of paramount concern. The doctor admin of a saloon car without any splint to his injured leg isters 50 mg of pethidine (meperidine) intramuscularly and had jolts of pain every time the car stopped on its. John is received by Dr Omoyemen, the attend tetanus toxoid is administered to prevent tetanus. Finally, while John is awaiting formal orthopedic Fracture immobilization on its own minimizes pain surgical review, his pain is reassessed regularly to deter due to the fracture injury by limiting movement of the mine the e? He is fully conscious, knows who he is, and their probable answers and is well oriented as to time and place. Dr Omoyemen obtains a brief caused by an infection, injury, or the progression of a history of the nature of the accident and proceeds to metabolic dysfunction or a degenerative condition. This material may be used for educational 115 and training purposes with proper citation of the source. Aisuodionoe-Shadrach several assessment tools have been designed to objec Although the multidimensional pain scale was tively measure it. Pain has multiple dimensions with developed for pain research, it can be adapted for use in several descriptions of its qualities, and its perception the clinic. This response could limit recovery from sur acute trauma and preoperative setting? Pain is not merely a clinical symptom but evi Furthermore, the sources of pain in acute trau dence of an underlying pathology. In the acute trauma ma and preoperative settings are mostly of deep somatic and preoperative setting, there is a temptation to over and visceral origin, as may occur in road tra? The in the acute trauma and preoperative settings is usually challenge is to help the health professional realize that the caused by a combination of various stimuli: mechanical, management of both symptoms (pain) and underlying thermal, and chemical. Tese stimuli cause the release pathology (acute appendicitis) should go hand in hand. Is pain an important issue to the patient who is Because of its complex subjectivity, pain is di? Freedom from pain can be considered a human However, a number of assessment tools have been de right. As fanciful as that may seem, it must be empha veloped and standardized to identify the type of pain, sized that pain is a natural accompaniment of acute quantify the intensity of pain, and evaluate the e? A pain scale may be either one-dimensional or mul In a study conducted at an accident and emer tidimensional. In the acute trauma/preoperative setting, gency room department of a university hospital in sub where the cause of pain is obvious and pain is expected Saharan Africa, 77% of patients who had preoperative to resolve more or less promptly, one-dimensional scales analgesia considered the analgesic dosage inadequate, are recommended. Often, paying attention to adequate analgesic tively impaired, and persons with language barriers. Nonpharmacological treatments may be helpful a fractured limb, the patient does not know the diagno but should not preclude drug treatment. Unrelieved pain may have negative physical and management of pain be instituted in the acute psychological consequences. Successful evaluation and management of pain treatment are to relieve pain as quickly as possible and is partly dependent on a positive relationship be prevent any adverse physical and psychological respons tween the patient and his or her relatives on the es to acute pain. Don?t believe that the ability to tolerate pain is a nurses play in ensuring that patients in this measure of ?manhood. It may not be practical to expect patients in the degree of pain using the following methodical ap acute trauma/preoperative setting to be absolute proaches: ly pain-free. Tropical Doctor odic intervals by the attending health professional with 2006;36:35?6. Preventing the development of chronic to the application of hot or cold compresses as needed. Avoid misconceptions and recognize culturally Pain: current understanding of assessment, management, and treatments. National Pharmaceutical Council and Joint Commission on Accredi tation of Healthcare Organizations. The perioperative period was uneventful, and the child (accompanied by his moth er) was discharged home, fully awake and comfortable Why is analgesia for minor about 5 hours after the procedure with a prescription surgical procedures a topic of oral paracetamol (acetaminophen). The mother In this section, I will explain why pain may be a com gave him the prescribed analgesic, but the pain per mon and signi? It is obvious that there are various options ing, not only to the patient but often to the whole house for providing e? For our illustrative case above, an example of a typical pharmacological analgesia therapy can be as fol What is minor surgery? Minor surgical procedures anesthetic is administered after induction of anesthe now constitute the majority of procedures carried out sia. This material may be used for educational 119 and training purposes with proper citation of the source. Gen respiratory depressant and sedative effects of erally, more than half or even two-thirds of all surgical opioid drugs outside of immediate supervised cases in health care facilities are usually considered mi medical care. Patients are often very anxious and dis criteria for selection for outpatient surgery is that pain tressed by the hospital and procedure experience, and should be minimal or easily treatable. For the same type of surgical procedure, pliance with the analgesic administration regimen. Unfortunately, when the patient is discharged, What factors lead to poor pain the intensity or continuity of pain care is disrupted. The pain of surgery often outlasts the pain medication or lo control after minor surgery? Contributory factors to poor postoperative pain control To avoid this problem, administer the? The pressures of current ambulatory surgical Preemptive analgesia implies that giving analgesia be practices, which emphasize rapid recovery and fore the noxious stimulus is more e? While this con sulting in anesthesia care givers and surgeons cept has not been convincingly proven in all clinical avoiding or minimizing the perioperative use of studies, what is clear is that more analgesia is often re potent and longer-lasting analgesics and sedatives quired to treat pain that is already established than to that may delay recovery and discharge. One Pain Management in Ambulatory/Day Surgery 121 should therefore aim to preempt or prevent pain if pos An often forgotten or neglected part of the sible or proactively treat pain as early as possible. Psychological and physical therapies comple Avoid analgesic gaps ment medications and should be used whenever possi Analgesic gaps subject the patient to recurring pain and ble. Such gaps tend to occur when ing painful areas, application of cold or hot compresses, the e? Psychological therapies in An appropriate dosing interval based on knowledge of clude behavioral and cognitive coping strategies such the pharmacology of the agent is important to minimize as psychological support and reassurance, guided imag this gap. Studies suggest Apply a multimodal analgesia strategy that these nonpharmacological therapies improve pain Multimodal analgesia implies the use of several analge scores and reduce analgesic consumption. In other intraoperative anesthetic requirements and facili words, the combination provides better analgesia than tate earlier recovery and discharge. Preven cially the long-acting ones like morphine and metha tion is better than cure. Much larger amounts of done, should preferably be avoided or used sparingly as an analgesic are required to treat established pain postoperative analgesics for minor surgery because of than to prevent it. J Anaesth 2001;87:73?87 in the analgesic ladder between the mild non-opioid [3] Shnaider I, Chung F. Tears at bedtime: a pitfall of extending paediatric day-case surgery without extending analgesia. Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings Chapter 17 Pharmacological Management of Pain in Obstetrics Katarina Jankovic Case report Systemic administration includes the intravenous, in tramuscular, and inhalation routes. As an example, an abnormal fetal pre patients in whom regional techniques are contraindicat sentation, such as occiput posterior, is associated with ed. What are the application routes A systematic review of randomized trials of for analgesia if needed? This material may be used for educational 123 and training purposes with proper citation of the source. Interest respiratory depression in the neonate is the primary ingly, midwifes have rated pethidine much better than reason for selecting a particular opioid. Regarding this parturients, probably because sedation was confused potential, pethidine (meperidine) may be preferred over with analgesia. Tese opioids If an anesthesiologist is not available, pethidine (me are not ?pure agonists of the mu-receptor, but mixed peridine) is usually the drug of choice. It remains the agonists and antagonists, which is the reason for their best investigated and most often used opioid in labor. The dose of pethidine commonly prescribed is 1 mg/ However, as with other opioids, respiratory kg i. To achieve tramuscular route is not recommended because it is that outcome in the neonate, it is recommended to not dependable?the rate of drug-absorption may vary. Higher doses have to teaching is that the neonate should be delivered within be strictly avoided, since pethidine may provoke sei 1 hour or more than 4 hours after the last pethidine zures. Pentazocine should not be used because of its Opioids cross the placenta and may a? This potential to cause dysphoria and sympathetic stimula is manifested in utero by changes in fetal heart rate pat tion. But ideally, naloxone?as most drugs in breastfeeding, but lack of data makes it advisable to pain management, should be titrated intravenously to rely on individual judgment, if only a limited number of its e? Breast-feeding during maternal treatment with If I have various opioids available, which one I paracetamol (acetaminophen) should be regarded as would choose, and why? Yes Meperidine (pethidine) 1 Neurobehavioral delay, sedation noted from longhalf-life metabolite; avoid. The use of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) in sin Nonopioid analgesics gle doses should not pose any signi? Aspirin, due to its causal association choice for pain management in breastfeeding postpar with Reye syndrome, generally is not recommended in tum women, as they do not a? Diclofenac suppositories are available in some drug is used commonly in obstetrics, such use is gain countries and are commonly used for postpartum ing disfavor as more sedation is reported in newborns. The possible advantages must be bal ratory acidosis, and abnormal neurobehavioral scores. Because of this prolonged half-life, neonatal Both pain and opioid analgesia can have a depression after exposure to pethidine may be profound negative impact on breastfeeding outcomes; thus, and prolonged.
The act requires that child care or less formed than usual for that child and not asso programs make reasonable accommodations for cIated with changes in diet treatment 11mm kidney stone dilantin 100 mg amex. Exclusion is required for all children with disabilities and/or chronic illnesses medications given to newborns order dilantin 100 mg without a prescription, diapered children whose stool is not contained in the dia considering each child individually symptoms kidney failure dogs cheap dilantin 100 mg line. In addition medications for adhd buy generic dilantin 100 mg online, diapered children with diarrhea should be excluded if the stool frequency exceeds two stools above normal for that child during the time in the program day treatment pancreatitis order on line dilantin, because this may cause too much work for 143 Chapter 3: Health Promotion and Protection the caregivers/teachers symptoms of buy dilantin 100 mg on-line, or those whose stool contains i. Readmission afer diarrhea can occur notifying the family at the end of the prior program when diapered children have their stool contained by the day. Rubella, until seven days afer the rash appears; Special circumstances that require specifc exclusion l. Pertussis, until fve days of appropriate antibiotic criteria include the following (2): treatment; A health care provider must clear the child or staf mem m. Children tion of the others in the group should be checked to be and staf members with Shigella should be excluded until sure everyone who was exposed has received the vaccine diarrhea resolves and test results from at least 1 stool culture or receives the vaccine immediately. Make decisions about caring for the child while await at least 48 hours afer antibiotics have stopped. Vomiting more than two times in the previous twenty symptoms the child is exhibiting. The child should be four hours, unless the vomiting is determined to be supervised by someone who knows the child well and caused by a non-infectious condition and the child who will continue to observe the child for new or wors remains adequately hydrated; ening symptoms. Abdominal pain that continues for more than two hours in their usual care setting while awaiting pick-up, the or intermittent pain associated with fever or other signs child should be separated from other children by at least or symptoms of illness; 3 feet until the child leaves to help minimize exposure of c. All who have been in contact with the ill child health department authority states that the child is must wash their hands. Toys, equipment, and surfaces noninfectious; used by the ill child should be cleaned and disinfected d. Rash with fever or behavioral changes, until the primary afer the child leaves; care provider has determined that the illness is not an b. Impetigo, only if child has not been treated afer notify should include onset time of symptoms, observations ing family at the end of the prior program day. The nature and severity of symp streptococcal infection), until the child has two doses toms and or requirements of the local or state health of antibiotic (one may be taken the day of exclusion department will determine the necessity of medical and the second just before returning the next day); consultation. Head lice, only if the child has not been treated afer of instructions are acceptable without an ofce visit; notifying the family at the end of the prior program c. As a child gets care do not necessarily need to have an in-person visit older s/he develops immunity to common infectious agents with a health care provider; and will become ill less ofen. In collaboration with the local health department, in preventing transmission of these organisms. Usually, the criteria in these department: two sources are more detailed than the state regulations so a. Chickenpox, until all lesions have dried and crusted, with specifc health training in performing this pro which usually occurs by six days; cedure and permission given by parents/guardians, c. Rash with fever or joint pain, until diagnosed not to accusations of sexual abuse; be measles or rubella; g. Only digital thermometers, not mercury thermometers, stools above normal for that individual or blood in should be used. Other types of Salmonella and Disinfecting do not require negative test results from stool cultures. Managing infectious diseases in child during the previous twenty-four hours, until vomit care and schools: A quick reference guide, 4th Edition. Scabies, until afer treatment has been completed; of the following conditions exists: o. Haemophilus infuenzae type b (Hib), prophylaxis, until cleared by the primary health care provider; a. This includes a respiratory illness in which the the symptoms of the staf member); staf member is unable to consistently manage respira tory secretions using proper cough and sneeze etiquette. Carefully observe hand hygiene policies; and temperatures are less accurate, but are a good option for 3. When using tympanic thermometers, too much earwax can cause the reading to be incorrect. A fully immunized child with a conta fore, tympanic thermometers should not be used in chil gious, infectious or communicable condition will likely dren under four months of age, where fever detection is not have an illness that is harmful to the child or others. Caregivers/teachers should be aware Book: 2015 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. In a systematic review, infrared ear thermometry for fever diagnosis (under the tongue) temperatures can be used for children in children fnds poor sensitivity. Facilities Tat Serve Children Who Are Ill Handwashing sinks should be stationed in each room that References 1. The facility may use a single kitchen for ill and well children if the kitchen is References 1. Children with chickenpox, pertussis, measles, mumps, Qualifcations of Directors of Facilities rubella, or diphtheria, require a room with separate ventilation including fresh outdoor air (1); That Care for Children Who Are Ill. Soap and disposable paper towels should be 149 Chapter 3: Health Promotion and Protection a. At least two prior years of satisfactory performance as Center, Large Family Child Care Home a director of a regular facility; c. Use of sanitizing chemicals; individual care and emotional support, who knows of 4. Ofer a program with trained personnel planned in illnesses, including: consultation with qualifed health care personnel and 1. Since illness tends to promote requirements; regression and dependency, children who are ill need a 5. Child Care Health Consultants for Facilities Caregivers/teachers have to be prepared for handling illness That Care for Children Who Are Ill and must understand their scope of work. Special training Each special facility that provides care for children who are is required of caregivers/teachers who work in special facili ill should use the services of a child care health consultant ties for children who are ill because the director and the for ongoing consultation on overall operation and develop caregivers/teachers are dealing with infectious diseases and ment of written policies relating to health care. Each care health consultant should have the knowledge, skills caregiver/teacher should have training to decrease the risk and preparation as stated in Standard 1. Plans for health care and for managing children with Child-Staf Ratios for Facilities That infectious diseases; Care for Children Who Are Ill d. The best interests of the child and 151 Chapter 3: Health Promotion and Protection family must be given primary consideration in the care of capacity for facilities that care for children who are ill, the children who are ill. Consultation by primary care provid child care health consultant with the local health authority ers, especially those whose specialty is pediatrics, is critical should review these plans and procedures annually in an in planning facilities for the care of children who are ill (1). Additional requirements should apply with sufcient staf and facilities to meet the needs of chil when children who are ill will be in care. State or local health department (especially public the following information on each child: health nursing, infectious disease, and epidemiology a. Upper or lower respiratory infection in which signs or Inclusion and Exclusion of Children from symptoms require a higher level of care than can be Facilities That Serve Children Who Are Ill appropriately provided; and Facilities that care for children who are ill who have condi m. A child care health Tese signs and symptoms may indicate a signifcant sys consultant can assist in arranging the evaluation. Red Book: frequency or is less formed in consistency than usual 2015 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. Exclude children whose stool frequency 153 Chapter 3: Health Promotion and Protection All medicines require clear, accurate instruction and medi 3. Prescription medications can ofen be timed to be given at home and this should be 3. It is important to make sure medication; the child isn?t receiving the same medications in two b. Telephone instructions Documentation that the medicine/agent is administered to from a primary care provider are acceptable if the care the child as prescribed is required. In the event medi facilities to be equipped, stafed, and monitored by the pri cation for a child becomes necessary during the day or in mary care provider capable of having the special health care the event of an emergency, administration instructions plan modifed as needed. They can also be very dangerous if the wrong type or wrong amount is given to the wrong person or at the wrong time. Prevention is the key to prevent poisonings by making sure medications are inaccessible to children. Adverse events undesirable substance such as used cofee grounds or from cough and cold medications in children. The trainer in medication administration should be a All medications, refrigerated or unrefrigerated, should: licensed health professional. Be kept in an organized fashion; skill and competency should be monitored annually or. Be stored at the proper temperature; ties with large numbers of children with special health care. In the event medication cannot be be trained to: returned to the parent or guardian, it should be disposed a. If there are community drug take back programs, or the separate written instructions in relation to the participate in those. State policies regarding nursing delegation and administration in child care settings: A case study. Safe medication administration in child care is extremely important and training of care 3. Tese laws guardian should observe; may include requirements for delegation of medication c. Pictures of skin lesions or skin condition may be health-policies and contains sample polices and forms helpful to parents/guardians. Resources for fact sheets and photographs include the 156 Caring for Our Children: National Health and Safety Performance Standards current edition of Managing Infectious Diseases in Child 3. Infectious Diseases That Require Disease surveillance and reporting to local health authori Parent/Guardian Notifcation ties is crucial to preventing and controlling diseases in the In cooperation with the child care regulatory authority and child care setting (2,3). Invasive infections; Ascertaining whether a child who is ill is attending a facil d. The child has any of the following conditions: fever, Appendix P: Situations that Require Medical Attention lethargy, irritability, persistent crying, difcult breath Right Away ing, or other manifestations of possible severe illness; References b. The child has tuberculosis that has not been evaluated; care and schools: A quick reference guide, 4th Edition. The facility should have a list of reportable diseases pro vided by the health department and should provide a copy 3. The plan should describe protocols the skin or mucous membranes or reduced urine output may program will follow and resources available for children, indicate dehydration, and the child should be medically families, and staf. Blood and/or mucus may indicate shig If a facility experiences the death of a child or adult, the ellosis or infection with E. The caregiver/teacher(s) responsible for any chil between parents/guardians, caregivers, health departments, dren who observed or were in the same room where and primary care providers (2). Minimal explanations should be If there is more than one case of vomiting in the facility, it provided until direction is received from the proper may indicate either contagious illness or food poisoning. The facility should inform parents/guardians and staf; parents/guardians that the program is required to report 8. Make resources for support available to staf, parents infectious diseases to the health department. Mulligan-Smith, Committee on Pediatric Emergency improved health and safety practices. Today there is a range of infant Feeding should occur in a relaxed and pleasant environ formulas on the market that vary in nutrient content and ment that fosters healthy digestion and positive social address specifc needs of individual infants. When infant formula is used to supplement an infant Feeding nutritious food everyday must be accompanied by being breastfed, the mother should be encouraged to con ofering appropriate daily physical activity and play time for tinue to breastfeed or to pump human milk since her milk the healthy physical, social, and emotional development of supply will decrease if her milk production isn?t stimulated infants and young children. The overall benefts of healthy eating behavior by early care and education staf practicing healthy eating patterns, while being physically helps a child to develop lifelong healthy eating habits. Active play and supervised structured ensure programs are ofering a variety of foods, selections physical activities promote healthy weight, improved over should be made from these groups of food: all ftness, including mental health, improved bone develop ment, cardiovascular health, and development of social a. The American Academy of Pediatrics, at risk for obesity or hypercholesterolemia, for children the United States Breastfeeding Committee, the Academy from one year of age up to two years of age; skim or 1% of Breastfeeding Medicine, the American Academy of for children two years or older, unsweetened low-fat Family Physicians, the World Health Organization, and the yogurt or low-fat cheese. Caregivers/ service standards, along with related appendixes, address teachers have a unique opportunity to support breastfeed age-appropriate foods and feeding techniques beginning ing mothers, who are ofen daunted by the prospect of with the very frst food, preferably human milk and when continuing to breastfeed as they return to work. The nutrition plan of attitudes about food, eating behavior, and consequently, should include steps to take when problems require rapid food habits. Responsive feeding, where the parents/ response by the staf, such as when a child chokes during guardians or caregivers/teachers recognize and respond mealtime or has an allergic reaction to a food. Sound food habits are built on eating and available to parents/guardians on request. Including culturally specifc family foods is a dietary goal for feeding infants If the facility is large enough to justify employment of a and young children. A written care plan from the pri physical activity on a daily basis promote a healthy mary health care provider, clearly stating the food(s) to be beginning during the early years and throughout the life avoided and food(s) to be substituted, should be on fle. Our overweight children: What parents, schools, and Because children grow and develop more rapidly during the communities can do to control the fatness epidemic. Children can learn healthy eating habits and be better equipped to maintain a healthy weight 163 Chapter 4: Nutrition and Food Service if they eat nourishing food while attending early care and 4. Excessive prompting, feeding in response to emo health care provider, children should be evaluated for tional distress, and using food as a reward have all been nutrition related medical problems, such as failure to shown to lead to excessive weight gain in children (5,6). For a child diagnosed as obese or Individual Children overweight, the plan would focus on controlling portion 4. Accessed September 7, 2017 larger sized portions and increased energy intake, prompt 2. Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health ing the importance of implementing proper portion sizing Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents. Caring ensures that food oferings are congruent with nutritional for Infants and Toddlers in Groups: Developmentally Appropriate Practice. Solid fats and added sugars may be included up to the daily maximum limit identifed in the 2015?2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Cheap 100mg dilantin with visa. Understanding the OCD Brain part 1: OCD and me.
References
- Jinnin M, Medici D, Park L, et al: Suppressed NFAT-dependent VEGFR1 expression and constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in infantile hemangioma, Nat Med 14(11):1236-1246, 2008 PMCID: 2593632.
- Pillai SG, Ge D, Zhu G, et al. A genomewide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): identification of two major susceptibility loci. PLoS Genet 2009;5 (3):e1000421.
- Ramachandran S, Temple B, Alexandrova AN, et al. Recognition of platinum-DNA adducts by HMGB1a. Biochemistry 2012;51(38):7608-7617.
- Shimony A, Filion KB, Mottillo S, Dourian T, Eisenberg MJ. Meta-analysis of usefulness of d-dimer to diagnose acute aortic dissection. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107(8):1227-1234.
- Kamran SC, Seisen T, Markt SC, et al. Contemporary treatment patterns and outcomes for clinical stage IS testicular cancer. Eur Urol 2018;72(2):262-270.
- Nathanson MH, Fredman B, Smith I, et al. Sevoflurane versus desflurane for outpatient anesthesia: a comparison of maintenance and recovery profiles. Anesth Analg 1995;81:1186- 1190.
- Katritsis DG, Ioannidis JP. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus conservative therapy in nonacute coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2005;111(22):2906-2912.
