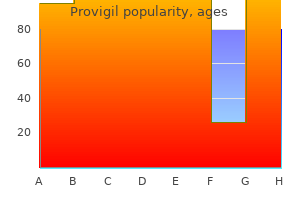
Provigil
Peter D. Beitsch, MD, FACS
- Director, Dallas Breast Center
- Department of Surgery
- Medical City Dallas Hospital
- Dallas, Texas
However insomnia psychology buy provigil 100 mg on-line, many older patients have difficulty learning how to cope with contact lenses sleep aid for 11 year old buy 200 mg provigil fast delivery. Cataract eyeglasses 25% larger can only be4 Field of vision: 4 than 1 combined with sleep aid that doesnt make you feel groggy 200 mg provigil with visa. The procedure on the fellow eye is performed after about a week if once the first eye has stabilized sleep aid kids buy cheap provigil 100 mg on line. Historical milestones: O Couching (reclination): For 2000 years until the 19th century, a pointed instrument was used to displace the lens into the vitreous body out of the visual axis. Daviel performed the first extracapsular cataract extraction by removing the contents of the lens through an inferior approach. Today intracapsular cataract extraction is used only with subluxation or dislocation of the lens. The entire lens is frozen in its capsule with a cryophake and removed from the eye through a large superior corneal incision (Fig. Then only the cortex and nucleus of the lens are removed (extracapsular extraction); the posterior capsule and zonule suspension remain intact. This provides a stable base for implantation of the posterior chamber intraocular lens. Extracapsular cataract extraction with implantation of a posterior chamber intraocular lens is now the method of choice. Then the softer portions of the cortex are removed by suction with an aspirator/irrigator attachment in an aspiration/irrigation maneuver. Where a tunnel technique is used to make this incision, no suture will be necessary as the wound will close itself. Extracapsular cataract extraction usually does not achieve the same broad exposure of the retina that intracapsular cataract extraction does, particularly where a secondary cataract is present. However, the extracapsular cataract extraction maintains the integrity of the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye, and the vitreous body cannot prolapse anteriorly as after intracapsular cataract extraction. Etiology: Extracapsular cataract extraction removes only the anterior central portion of the capsule and leaves epithelial cells of the lens intact along with remnants of the capsule. These epithelial cells are capable of reproducing and can produce a secondary cataract of fibrous or regenerative tissue in the posterior capsule that diminishes visual acuity (Fig. O Oculodigital phenomenon: the child presses his or her finger against the eye or eyes because this can produce light patterns the child finds interesting. Operate as early as possible: Retinal fixation and cortical visual responses develop within the first six months of life. This means that children who undergo surgery after the age of one year have significantly poorer chances of developing normal vision. Children with congenital cataract should undergo surgery as early as possible to avoid amblyopia. The prognosis for successful surgery is less favorable for unilateral cataracts than for bilateral cataracts. This is because the amblyopia of the cataract eye puts it at an irreversible disadvantage in comparison with the fellow eye as the child learns how to see. Therefore, the procedure should include a posterior capsulotomy with anterior vitrectomy to ensure an unobstructed visual axis. The operation preserves the equatorial portions of the capsule to permit subsequent implantation of a posterior chamber intraocular lens in later years. Refraction changes constantly: the refractive power of the eye changes dramatically within a short period of time as the eye grows. Refractive compensation for a unilateral cataract is achieved with a soft contact lens (Fig. Refractive correction of bilateral cataracts is achieved with cataract eyeglasses. Refraction should be evaluated by retinoscopy (see Chapter 16) every two months during the first year of life and every three to four months during the second year, and contact lenses and eyeglasses should be changed accordingly. Implantation of posterior chamber intraocular lenses for congenital cataract is not yet recommended in children under three years of age. This is because experience with the posterior chamber intraocular lens and present follow-up periods are significantly less than the life expectancy of the children. In addition, there is no way to adapt the refractive power of the lens to changing refraction of the eye as the child grows. Regular evaluation of retinal fixation is indicated, as is amblyopia treatment (see patching). O Luxation (complete dislocation): the lens is torn completely free and has migrated into the vitreous body or, less frequently, into the anterior chamber. Later in life, pseudoexfoliation may also lead to subluxation or luxation of the lens. Hereditary causes and metabolic disease produce lens displacement early yet on the whole are rare. Additional rare causes include hyperlysinemia (characterized by retarded mental development and seizures) and sulfite oxidase deficiency (which leads to mental retardation and excretion of cysteine in the urine). Symptoms: Slight displacement may be of no functional significance to the patient. More pronounced displacement produces severe optical distortion with loss of visual acuity. Diagnostic considerations: Cardinal symptoms includetremulousmotion of the iris and lens when the eye moves (iridodonesis and phacodonesis). Treatment: Optical considerations (see symptoms) and the risk of secondary angle closure glaucoma from protrusion of the iris and dislocation of the lens into the anterior chamber are indications for removal of the lens. As the zonule fibers are intact, a certain measure of accommodation is still possible. The uveal tract consists of the following structures: O Iris, O Ciliary body, O Choroid. Neurovascular supply: Arterial supply to the uveal tract is provided by the ophthalmic artery. O the short posterior ciliary arteries enter the eyeball with the optic nerve and supply the choroid. O the long posterior ciliary arteries course along the interior surface of the sclera to the ciliary body and the iris. They form the major arterial circle at the root of the iris and the minor arterial circle in the collarette of the iris. The anterior ciliary arteries originate from the vessels of the rectus muscles and communicate with the posterior ciliary vessels. Venous blood drains through four to eight vorticose or vortex veins that penetrate the sclera posterior to the equator and join the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins (Fig. The posterior layer is opaque and protects the eye against excessive incident light. The anterior surface of the lens and the pigmented layer are so close together near the pupil that they can easily form adhesions in inflammation. Minor arterial circle of the iris (collarette of the iris) Major arterial circle of the iris Anterior ciliary artery Long posterior ciliary artery Vorticose vein Short posterior ciliary artery Fig. The collarette of the iris covering the minor arterial circle of the iris divides the stroma into pupillary and ciliary portions. The pupillary portion contains the sphincter muscle, which is supplied by parasympathetic nerve fibers, and the dilator pupillae muscle, supplied by sympathetic nerve fibers.
A degenerative (black) lesion indicates major toxic build-up and degeneration insomnia 64 order provigil canada, and the other two lesions sleep aid without antihistamine purchase genuine provigil on line, sub-acute (light-grey) and chronic (dark-grey) sleep aid pills provigil 100mg on-line, fall between these other two (Bamer sleep aid list cheap provigil generic, 1996). All white acute (over-activity) In the final step the area returns to its former colour. But in the case of complete surgical removal of an organ, the iris manifests the condition prior to anaesthetic administration. Another article published in Australian Doctor (2003), cites studies from peerreviewed journals. The photographs were randomly coded and evaluated by five Dutch iridologists, the results of which was that the statistical significance was also no better than chance. Another recent study found iridology of no value in the diagnosis of various common cancers, with a sensitivity of 0. One hundred-and-ten patients participated in the study, of which 68 had histologically proven cancers of the breast, ovary, uterus, prostate or colorectum. All participants were evaluated by an iridologist, who was blinded to medical history and gender. Photographs of 57 hospitalized patients were taken, in combination with their medical records, and submitted for computerized processing. The researchers concluded that iridology can be extremely useful in the diagnosis of specific general pathology (Demea, 2002). In another recent study by Stearn & Swanepoel (2006) by the University of Pretoria, iridology was deemed effective at diagnosing moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss in adolescents. The photographs were randomized and then given to an iridologist (which was blinded) for evaluation. A 70% correct identification rate was obtained, indicating a statistically significant relationship. Finally, a systematic literature review on publications and opinions on iridology for the period from 1970 to 2005, was conducted by the University of Sao Paulo. Fifteen articles were in favour of the iridological method and ten against it (Salles et al. Anatomically, the iris, together with the ciliary body and the choroid, is found in the intermediate layer of the eye wall (as can be seen in Figure 2. The uvea is sandwiched between the outer fibrous tunic and the inner neural tunic or retina (Martini, 2006). From anterior to posterior, the layers are: the anterior border layer, the iris stroma, the dual pupillary muscle layer (combining both the sphincter and dilator muscles) and the posterior epithelium, in that order (Oyster, 1999). The iris root is the junction of the iris and the ciliary body, and is the thinnest part. It is here where damage to the iris occurs most commonly during trauma, severing its attachment. The thickest part is two-thirds from iris root to pupil margin and is called the collarette, which is also the site of the minor arterial circle. It divides the iris into pupillary and ciliary regions, containing the sphincter and dilator muscles, respectively (Oyster, 1999). The fibroblasts tend to congregate on the surface, forming a subdivision between them and the melanocytes below. This meshwork generally weaves itself in a radial fashion away from the pupil (Oyster, 1999). They are remarkable in that they vary between irises and that aqueous can flow freely from the anterior chamber to the inner stroma through them (Oyster, 1999). The pupillary ruff or frill is the ring of dark pigment surrounding the margin of the pupil. It is formed by the posterior epithelial layer as it folds around the inside edge of the pupil. Contraction folds are prominent circular lines that appear on the surface of the iris when the pupil is dilated (Oyster, 1999). Iris processes are extensions of the anterior border layer that run from it to the trabecular meshwork, and are made up of cells from both layers (Oyster, 1999). A significant portion is basically open space filled with aqueous in vivo, while the rest consists of a loose arrangement of the same components of the previous layer (fibroblasts, melanocytes and collagen fibers). The only other important additions to this layer are blood vessels and fine nerve fibers (Oyster, 1999). The arteries arise from major and intramuscular arterial circles in the ciliary body, and the veins drain through ciliary processes into the vortex veins. The sphincter group is organized as a series of concentric rings around the pupil and innervated by the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system. The dilator group extends radially away from the edge of the pupil and is innervated by the sympathetic branch (Martini, 2006). The sphincter is substantially thicker than the dilator and the muscles are not connected, except for a few muscle fiber strands (Oyster, 1999). Although both epithelial layers are pigmented, the anterior epithelium has less pigment and is myoepithelium from which the dilator muscle arises. The posterior epithelium is the major lightabsorbing layer in the iris (Oyster, 1999). Neuroectoderm of the brain (from which develops the retina, posterior epithelium of the iris and optic nerve) 2. The dilator and sphincter pupillae muscles are finally derived from the neuroectoderm of the optic cup appearing to stem from the anterior epithelial cells, which consequently differentiate into smooth muscle cells (Moore & Persaud, 2003). Congenital disorders of the iris and cornea (iridocorneal dysgenesis) are multiple and tend to overlap significantly. It is ascribed to failure of the rim of the optic cup to proliferate (Moore & Persaud, 2007). This rare bilateral anomaly can be divided into the following four phenotypes, according to Kanski (1994): 1. The appearance of the pupil is either distorted by strands of the post-natal remnant tissues or almost completely occluded (Yanoff & Sassani, 2009). A coloboma is an otherwise normal iris with abnormal sectors or holes, giving it a key-hole appearance (Moore & Persaud, 2007), and is illustrated in Figure 2. It may be confined to the iris or project into the ciliary body and retina (Oyster, 1999). A typical or simple coloboma is situated in the inferior sector of the iris (Figure 2. It is commonly hereditary with autosomal dominant transmission (Moore & Persaud, 2007). Defects may appear as an area of sparse, inadequately formed stroma and not as a total want of tissue (Oyster, 1999). Complete or full-thickness holes extending through the iris is another developmental anomaly and is called pseudopolycoria (Kanski, 1994). It is generally symmetrical and bilateral, albeit the decentralisation and direction may be markedly different between both eyes. Any deviations from the normal iris with a central circular pupil are optically insubordinate (Oyster, 1999). Heterochromia iridum is a difference in colour between two irises of the same individual. Heterochromia iridis is a sectoral difference in colour in the same iris (Yanoff & Sassani, 2009).
Nitrate removal methods include ion exchange (normally for groundwaters) and biological denitrifcation (normally for surface waters) insomnia auburn order provigil line. However insomnia shop sofia order genuine provigil on-line, there are disadvantages associated with both approaches sleep aid elderly order 100 mg provigil overnight delivery, including the need for regeneration and disposal of spent regenerant with ion exchange sleep aid zeppelin purchase generic provigil canada, the complexities of operation and the potential for microbial and carbon feed contamination of the fnal water with biological denitrifcation. Care should be taken with the use of chloramination for providing a residual disinfectant in the distribution system. It is important to manage this to minimize nitrite formation, either in the main distribution system or in the distribution systems of buildings where chloramines are used to control Legionella. It is of low acute toxicity to experimental animals, but it has been shown to produce kidney tumours in rodents following longterm exposure to doses higher than those required to produce nephrotoxicity. It is not genotoxic, and the reported induction of tumours is believed to be due to cytotoxicity resulting from the chelation of divalent cations such as zinc and calcium in the urinary tract, leading to the development of hyperplasia and subsequently neoplasia. Nitrobenzene Nitrobenzene is used primarily in the production of aniline, but it is also used as a solvent, as an ingredient of metal polishes and soaps and in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including acetaminophen. Concentrations of nitrobenzene in environmental samples, such as surface water, groundwater and air, are generally low, except in areas with industrial pollution. Based on limited data, it appears that the potential for contamination is greater for groundwater than for surface water. The general population can be exposed to variable concentrations of nitrobenzene in air and possibly drinking-water. Only populations in the vicinity of manufacturing activities and petroleum refning plants are likely to have any signifcant exposure to nitrobenzene; however, people living in and around abandoned hazardous waste sites may also have potential for higher exposure, due to possible groundwater and soil contamination and uptake of nitrobenzene by plants. The main systemic effect associated with human exposure to nitrobenzene is methaemoglobinaemia. Although some recent studies have reported positive results in mutagenicity tests, it cannot be excluded that nitrobenzene is a non-genotoxic chemical. Because nitrobenzene occurrence in drinking-water at concentrations above trace levels is infrequent, it is not considered necessary to derive a formal guideline value. However, health-based values can be calculated to provide guidance in the event 404 12. It should be emphasized that the derivation of the long-term health-based values includes large uncertainties because of the dose metric conversion from inhalation studies and the possibility of increased metabolism to aniline in the gastrointestinal tract. It should be emphasized that nitrobenzene is a potent methaemoglobinaemic agent in humans, which is of particular concern for bottle-fed infants. Currently, data are not adequate to determine a separate health-based value for this end-point. As a consequence of the clear evidence of carcinogenicity, there have been few studies of other possible toxicity end-points. Activation by liver microsomal S9 fractions is necessary for a positive in vitro result. It is used as a fumigant and acaricide and as a pre-harvest soil and foliage treatment on a wide variety of crops, both outdoors and in greenhouses. Parathion released to the environment will adsorb strongly to the top layer of soil and is not likely to leach signifcantly. As the health-based value is much higher than concentrations of parathion likely to be found in drinking-water, the presence of parathion in drinking-water under usual conditions is unlikely to represent a hazard to human health. For this reason, the establishment of a formal guideline value for parathion is not deemed necessary. The leaching potential of pendimethalin appears to be very low, but little is known about its more polar degradation products. In a long-term dietary study, some toxic effects (hyperglycaemia in the mouse and hepatotoxicity in the rat) were present even at the lowest dose level. On the basis of available data, pendimethalin does not appear to have signifcant mutagenic activity. Long-term studies in mice and rats have not provided evidence of carcinogenicity; however, these studies have some important methodological limitations. Conclusive evidence of carcinogenicity has been obtained in one animal species (mice). Petroleum products Petroleum products are used in large quantities, primarily as fuels. They are complex mixtures of chemicals derived from crude oil by distillation and fractionation. They consist primarily of a wide range of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, many of which are of extremely low solubility in water. The primary concern for drinking-water is the potential for spills into source water, penetration of distribution systems and contamination of drinking-water treatment works. Substances such as the alkyl benzenes and the alkyl naphthalenes have taste and odour thresholds of a few micrograms per litre. In view of the above, it is not considered appropriate to set a formal health-based guideline value for petroleum products in drinking-water. In the event of a spill, it may be necessary to carry out a context-specifc assessment of the risk to health. The fact that petroleum products are complex mixtures of many individual hydrocarbons is a complicating factor in determining the potential risks to consumers. The traditional approach of evaluating individual chemicals in assessing the risks from drinking-water is therefore largely inappropriate. In order to overcome this diffculty, it is more practical to consider a series of hydrocarbon fractions and to determine appropriate tolerable concentrations for those fractions. This pragmatic approach provides a suitable basis for assessing the potential health risks associated with larger-scale contamination of drinking-water by petroleum products. Although the approach is based on the analysis of hydrocarbon fractions, most are of low solubility, and the most soluble fractions, consisting largely of lower molecular weight aromatic hydrocarbons, will be present in the greatest concentration. Although pH usually has no direct impact on consumers, it is one of the most important operational water quality parameters (see chapter 10). It is also used as a general surface disinfectant in hospitals, nursing homes, veterinary hospitals, poultry farms, dairy farms, commercial laundries, barbershops and food processing plants. Both 2-phenylphenol and its sodium salt are carcinogenic in male rats, and 2-phenylphenol is carcinogenic in male mice. However, urinary bladder tumours observed in male rats and liver tumours observed in male mice exposed to 2-phenylphenol appear to be threshold phenomena that are species and sex specifc. Because of its low toxicity, however, the health-based value derived for 2-phenylphenol is much higher than concentrations of 2-phenylphenol likely to be found in drinking-water. Under usual conditions, therefore, the presence of 2-phenylphenol in drinking-water is unlikely to represent a hazard to human health. For this reason, the establishment of a formal guideline value for 2-phenylphenol is not deemed necessary. Owing to their low solubility and high affnity for particulate matter, they are not usually found in water in notable concentrations. However, this health-based value is signifcantly above the concentrations normally found in drinking-water. Under usual conditions, therefore, the presence of fuoranthene in drinking-water does not represent a hazard to human health. For this reason, the establishment of a formal guideline value for fuoranthene is not deemed necessary. Potassium Potassium is an essential element in humans and is seldom, if ever, found in drinkingwater at levels that could be a concern for healthy humans. It can also occur in drinking-water as a consequence of the use of potassium permanganate as an oxidant in water treatment. In some countries, potassium chloride is being used in ion exchange for household water softening in place of, or mixed with, sodium chloride, so potassium ions would exchange with calcium and magnesium ions.
In girls insomnia yahoo purchase provigil 100 mg overnight delivery, may have lack of onset of secondnormal variants of premature thelarche (isoary sex characteristics and amenorhea due lated premature breast development) and to primary ovarian failure (due to gonadal pubarche (early pubic hair development) in dysgenesis sleep aid industry cheap provigil generic, enzyme defects qc sleep aid purchase provigil master card, infection sleep aid otc cheap provigil uk, surgirls from pathologic causes; distinguish norgery, radiation, chemotherapy, etc. May have normal or abnormal genitalia may have incomplete virilization depending on underlying etiology of pubertal 3. With precocious puberty, may have tall stature, tumor) or dysfunction (see growth disturpremature secondary sex characteristics bances this chapter) 4. With delayed or interrupted pubertal develto 66% of normal boys during puberty; onset opment may have findings consistent with between 10 and 12 years, peak occurrence 13 endocrine disorder. Physician consultation or referral to pediat2 weeks ric endocrinologist for suspected pathologic 2. Treatment dictated by identified etiology underlying tissue; typically breasts unequal for pathologic cause of pubertal delay or in size and 3 cm in diameter; breasts may abnormality in pubertal development. Management of underlying endocrine disoropment with testes 3 cm length ders and diseases and systemic illness. Pubertal (physiologic) gynecomastia 4 cmdisorders or tumors; chromosomal abnorexplanation, reassurance, and observation; malities. Pharmacologic agents (discontinuance of required as regression rare, especially if gynebirth control pills, use of tranquilizers) comastia present for 4 years; pharmacologic d. Gynecomastia usually very upsetting to adoweight loss lescent but often not discussed because of. Uterine dysfunction after abortion, infecembarrassment; reassure about transience and tion, C-section spontaneous regression f. Majority of obesity in adulthood has orisigns of chronic, systemic illness or syndromes gins in childhood. Current prevalence ranges 5% to 10% in some short stature); may show signs of pregnancy African and Asian countries to 75% in urban 2. May have lack of development of secondary Samoa characteristics or normal sexual development 2. Obesity is associated with subclinical chronic reproductive endocrinologist, surgeon, pediatinfiammation, increased insulin resistance, ric neurologist, obstetrician, psychologist) early atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, 3. Treatment directed at management or cornonalcoholic fatty liver disease, polycystic rection of underlying cause of abnormal ovary syndrome, infertility in older adolesmenstrual processes. Genetic counseling may be indicated if genetic triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein; also etiology decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein 3. Degree of somatic overweight that causes detnutritional deficits, especially iron rimental health consequences 2. Comorbidities include hyperlipidemia, hyperrelated to race, ethnicity, and socioeconomics tension, hepatic stenosis, polycystic ovary 3. Dietary history, pubertal status, affect/school advanced laparoscopic skills; common performance complications include iron deficiency, 3. Secondary hypothyroidism results from: fasting glucose and insulin level, HbA1c; also a. Severe obesity in toddler may require genetics or pituitary gland compromising thyroid testing and leptin levels function 3. Congenital hypothyroidism has a higher incidence in which of the following populationsfi The most common cause of hyperthyroidism in vigorous activity children and adolescents is: d. A 14-year-old adolescent female who is heat intolerant and has amenorrhea Questions 345 c. Is caused by anatomic defects in the brain precocity or incomplete (pseudoprecocity)fi True precocity occurs because of hormonal hypothalamus stimulation from the pituitary or hypob. Results from damage to the hypothalamus thalamus causing gonadal maturation and or pituitary from surgical trauma or infection fertility c. Incomplete precocity is caused by adrenal symptom or gonadal tumor or dysfunction and results 9. An infant with polydipsia, polyuria, irritability, in increased linear growth but no developand failure to thrive, should be evaluated for: ment of secondary sex characteristics d. Hyperglycemia arm span, arachnodactyly, laxity of joints, pectus excavatum, and an abnormal echocardiogram 10. Which one of the following is not characteristic would be suspected of having: of constitutional growth delayfi Prominent mandible and supraorbital ridge and microphallus should be suspected of having: c. Increased pigmentation in the axilla, groin, ondary sex characteristics at puberty and who areola, hand creases, and in surgical scars has small, underdeveloped testes should be susc. Which finding is not a sign or symptom of diacharacteristics betes onset in childrenfi
Order provigil cheap online. 4 hours of rain and thunder real storm sound for good sleep |Thunderstorm #1.