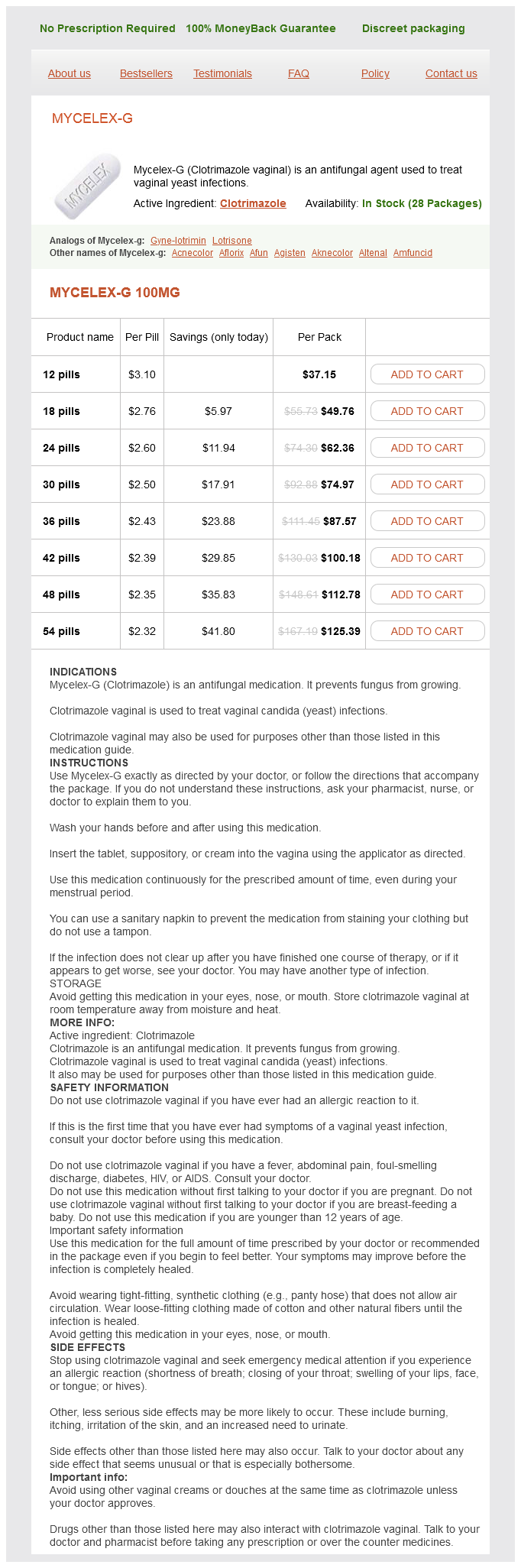
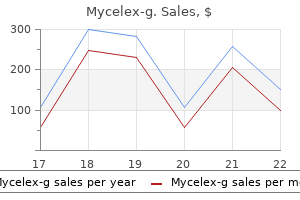
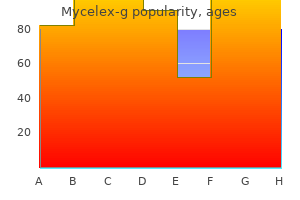
Mycelex-g
Randall Kevin Wolf, MD
- Director
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Deaconess Hospital
- Cincinnati, Ohio
Warm milk contains suffient L-tryptophan to account for its historical use as a soporific: carbohydrates (cookies) increase L tryptophan absorption fungus the bogeyman purchase mycelex-g australia. L-tryptophan has been associated with an eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome with an increase in white blood cells (> 2 antifungal questions order mycelex-g 100mg otc, 000 eosinophils/ml) anti yeast remedies order mycelex-g 100 mg amex, joint pains fungus gnats kitchen 100 mg mycelex-g mastercard, 3667 swelling of the arms and legs fungus gnats in hydro discount mycelex-g 100mg otc, skin rash/sclerosis fungus on tree trunk buy mycelex-g 100mg line, and pyrexia. Anginal exacerbation and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation have been reported in elderly patients. Minaprine, an amino-phenylpyridazine, has little anticholinergic, cardiotoxic, sedative, or weight promoting properties. Psychotic symptoms can occur (Howard 3671 & Warnock, 1999) and derive from dopaminergic stimulation. Metabolites of bupropion may yield false-positive results for amphetamine in urine as the chemical 3672 structure of this unicyclic drug resembles that of amphetamine. Bupropion, used in low dosage, may attenuate the sexual dysfunction caused by other medication. Its dopaminergic effects account for its use (in lower doses than for depression: Leonard, 2007) as an aid in smoking cessation. Resistant depression the occasional depressive does not respond to any of the above drugs. The diagnosis should be reviewed and any missed clue sought, such as social or personality difficulties. The trial was 3668 the most likely explanation seems to be that a change in the production process (less powdered carbon) in a Tokyo company led to contamination with strain V of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. A similar syndrome, toxic oil syndrome, followed ingestion of contaminated olive oil. In patients with end-stage renal disease these metabolites may accumulate and cause seizures. Ninety-two patients entered and significantly fewer on active therapy relapsed during the six months: 22% compared with 50% of those on placebo. An interesting finding was that more people complained of dry mouths than could be attributed to the active drugs. Very high doses of antipsychotic drugs, once commonly employed, should only be resorted to as a last resort. Plasma levels of 3675 chlorpromazine correlate poorly with therapeutic effect and better with prolactin 3676 secretion. However, according to Volavka ea, (1995) plasma levels of haloperidol up to c 12 ng/ml may correlate with antipsychotic effect for the first few months (5-20 ng/ml according to other authors), whereas a lower level may improve negative symptoms thereafter. Phenothiazine dyes were developed for commercial use in the 1880s and chlorpromazine is a derivative of such compounds. Clozapine, in terms of weight gain is the main offender, followed in descending order by olanzapine, sertindole, risperidone, and ziprasidone. However, haloperidol may be associated with slower (over a year) and equally significant weight gain. Zipursky ea (2005) found significant weight gain in patients treated with olanzapine or haloperidol. Weight and blood glucose monitoring of in-patients is the exception rather than the rule. No drug of any type to which a patient has shown hypersensitivity should be given to such a patient. In reality, atypical drugs can raise prolactin levels but differ in degree and duration of dose-dependent prolactin elevation (risperidone > olanzapine or clozapine) due to differential binding properties of each drug on pituitary D2 receptors. However, Meaney ea (2004) found reduced mineral density in schizophrenic subjects on longterm prolactin-raising antipsychotic drugs and lower testosterone levels in men was associated with reduced bone mineral density; but the study contained no comparison group and the females were past the menopause so that associations with gonadal status could not be measured. If the level exceeds 100 ng/ml, consider endocrinological referral to outrule a pituitary adenoma. However, antipsychotics, by blocking hypothalamic receptors, interfere with this message from circulating leptin. The 7-hydroxy derivative has therapeutic properties but the sulphoxide is inactive. This has a series of effects leading to the opening of other channels through which potassium ions move out of the cell. Sulpiride will decrease hyperpolarisation as an acute neuroleptic defect, but with chronic application of a neuroleptic rebound hyperpolarisation occurs. Rebound over activation of such systems roughly parallels clinical improvement after days to weeks, and the net effect is that such neurones (in the 3684 rat) become less sensitive to environmental stimulation. Blockade of D2 receptors is 3685 thought to provide the therapeutic effect of typical antipsychotic drugs. Post-synaptic D2 receptor agonists, such as bromocriptine, can potentially precipitate a psychosis, even in persons without a prior history. Secondary negative symptoms, such as mutism and social withdrawal secondary to 3688 3689 positive psychotic phenomena, tend to improve with treatment. Also, most antipsychotics have active metabolites with half-lives longer than the parent compounds, so relapse may be delayed for months in some cases after the drug is stopped. The presence of active metabolites and the accumulation of drug in adipose tissue have made it impossible to produce a reliable dose-response curve for neuroleptics. Tachycardia from antipsychotic medication may arise from anticholinergic or postural hypotensive actions. Amongst the advantages are a short duration of action and an increased flexibility of dose in the short term. Phenothiazines have a three-ring nucleus and members of the family differing in the side chains that are joined to the N atom in the middle ring. The ester is released from the oil phase by slow diffusion into the body water phase. Direct or indirect evidence of depot antipsychotic drugs can be found in the body up to 6 months after administration of the drug was stopped. It has very little affinity for central histamine receptors, which may account for its relatively weak sedative effect. The main uses of droperidol were its use in conjunction with narcotic analgesics in neuroleptanalgesia; as a premedication alone or with a narcotic analgesic; and in the acute management of the agitated manic patient. Longer-lasting depot neuroleptics can and have been started simultaneously with zuclopenthixol acetate. Fluspiriline (Redeptin, a phenylbutyl piperidine) 2 mg test dose, weekly injections (may get local fibrotic nodules). Olanzapine palmoate (Zypadhera) Risperidone depot see below under atypical drugs. Use is now restricted to second line treatment of adult cases of schizophrenia under the supervision of a consultant psychiatrist. Other conditions/medicines that lead to electrolyte imbalance may increase the risk for serious cardiac arrhythmias. As of December 2000, Novartis limited the use of thioridazine (Melleril) to adult schizophrenia under the supervision of a consultant psychiatrist. The combination of pimozide and fluoxetine can lead to bradycardia and/or delirium. Do not combine pimozide and other calcium channel blocking drugs, such as nifedipine, diltiazem, and verapamil. Atypical antipsychotic drugs may carry similar risk for sudden death as do the typical (older) drugs. Special caution is required in cases with renal disease, cardiovascular disorder, Parkinsonism, epilepsy, and serious infection. Prochlorperazine (Stemetil) has little or no antipsychotic actions and is mainly used as a sedative or antiemetic. Furthermore, postsynaptic D2 receptors (implicated in schizophrenia) are blocked, whereas D1 receptors function normally. Loxapine (Loxapac), a tricyclic dibenzoxazepine like amoxapine with some structural similarity to phenothiazines and carbamazepine, is started at 20-50 mg/day in two doses. It is increased over 7-10 days to 60-100 mg/day, given twice to four times per day. The usual maintenance dose is 20-100 mg/day, and the maximum daily dose is 250 mgs. According to Buckley and McManus, (1998) loxapine had the highest fatal toxicity index 3697 (deaths due to poisoning) of all antipsychotics. Hummer ea (2005) used dual x-ray absorptiometry to determine bone mineral density and that male schizophrenics, but not females with that diagnosis, had low mineral density in the lumbar region. Regular review of antipsychotic prescriptions are necessary in nursing homes and elsewhere. Adding an H2 blocking agent or sibutramine (Henderson ea, 2005) has been suggested to reduce weight gain in patients on olanzapine. Poyurovsky ea(2003) report that reboxetine may attenuate weight gain in olanzapine-treated schizophrenics. Metformin (inhibits hepatic glucose production) is reported to abrogate weight gain, decreased insulin sensitivity, and abnormal glucose metabolism due to atypical antipsychotics. Atypical-treated patients may be tested more often for diabetes than those treated with typical drugs. Without dismissing concerns about pharmacological over-control in nursing homes, such research does not control for the underlying cause of behavioural problems in demented patients. They develop over 1-3 days and tend to subside in about a week, or up to 3 weeks with depot preparations. Asthmatic receiving antipsychotics may require episodic beta adrenergic medication and should be aware of the potential dangers of receiving adrenaline during acute attacks. The main differential diagnoses to consider in cases of tetanus are tetany, strychnine poisoning, phenothiazine toxicity, and meningitis. Complications include metabolic acidosis, dehydration, shock, coagulopathy, acute myoglobinuria and renal failure, respiratory failure and pneumonia, and cerebellar damage. Dantrolene (Dantrium, 10 mgs/Kg/day) acts peripherally to reduce skeletal muscle tone. A clustering of cases in South Wales during the early 1990s added to the aetiological debate. Akinesia is a very common and usually extremely early adverse effect of antipsychotic medication. Sustained contraction of muscles of neck, mouth, tongue, or occasionally other muscle groups that is subjectively distressing and 3728 3729 often painful. Examples are oculogyric crisis, blepharospam, glossopharnygeal 3730 dystonia, tortipelvis, lordosis, scoliosis, opisthotonus, and twisting of mouth or 3731 rotation of neck. Acute first-episode psychotic patients are more likely to develop acute 3732 dystonia if they are relatively young and have negative symptoms. The young male (well muscled) is the classic victim but the association with male sex is questionable. Reducing the dose of antipsychotic drug may lead to a transient worsening of dystonic movement, but about 50% of the movements will improve or disappear eventually. Median of 5 years exposure to antipsychotic drugs but can occur as early as 3 weeks. Anticholinergic drugs, tetrabenazine, reserpine, clozapine, or stopping the offending drug are all possible management strategies. Thornton & McKenna, 1994) 3730 Dysarthria, dysphagia, breathing problems, cyanosis. Botulinum toxin can be used for circumscribed tardive dystonic syndromes, such as laryngeal dystonia, but injections need to be repeated every 3-6 months. Thalamotomy, pallidotomy, and deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus are surgical approaches to managing refractory cases. Tardive dysbehaviour disorder, the occurrence of increased activity, aggression, screaming, insomnia and so on after stopping long-term antipsychotic drug treatment, (Gualtieri ea, 1984) is another controversial disorder. Akathisia May be responsible for non-compliance with medication, violence or even suicide Occurs in both medicated and unmedicated Parkinsonism Occurs in about 20% (12. There may be subjective and objective components, but the absence of the subjective element (pseudoakathisia) does not negate the diagnosis, (Sachdev, 2004, p. However, the supine case may still show legs crossing and uncrossing, shifting of the position of the trunk, and various other movements. Akathisia was first reported as a complication of antipsychotic medication by Hans Steck (1954) a psychiatrist at Cery-Lausanne. Withdrawal akathisia develops days to weeks after stopping or reducing the dose of an antipsychotic drug. However, akathisia following removal of a drug that suppresses akathisia does not fit this definition. Also, pain or burning in the oral or genital reasons has been included in this category.
Culture results can take anywhere formis is the causative agent of rat bite fever antifungal for diaper rash generic mycelex-g 100mg with mastercard. Findings with sickle cell anemia also have functional from asymptomatic secretion of organisms asplenia and are more susceptible to infections to chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive are caused by encapsulated organisms fungus natural treatment 100mg mycelex-g visa. Nontypeable H influenzae for annual influenza immunization has been is also a common cause antifungal kit by bioactive nutrients purchase genuine mycelex-g online, but since the advent of expanded to include all children 6 months Hib vaccine H influenzae type B is rarely seen anti fungal nappy rash cream purchase cheapest mycelex-g. Initial therapy for acute sinusitis should be with an agent of the narrowest spectrum 81 tree fungus definition purchase mycelex-g 100mg with visa. Amphotericin B and the portal of bacterial entry that subsequently itraconazole are effective therapies fungus gnats cinnamon buy mycelex-g 100mg cheap, but more ulcerates. Painful, regional lymphadenopathy is broad spectrum, and not necessary for this patient. The tests performed within the first few months of rash that accompanies R typhi (endemic age and a third performed at 4 months of age typhus) is maculopapular and can occur over or greater are all negative. Rickettsia prowazekii (epidemic typhus) confers Western blot is used as a confirmatory test in a rash that begins on the trunk and spreads to patients who are older than 18 months. It is also associ thymocyte and immature B-cell death from ated with many other organisms. Erythema toxicum is a function that occurs in about 1/50, 000 live common newborn rash with eosinophilic pus births. Parenteral age 12 months, followed by a second dose in 6 penicillin remains the preferred treatment. S pneumoniae does not have pres Both thick and thin films should be examined, ence of the mef gene. The thin film is useful for species identi dose overwhelms the penicillin-binding pro fication as well. Clindamycin recovery when joint fluid is inoculated into a is most active against gram-positive organisms blood culture bottle, and held for at least 7 days. The other choices available S aureus and S pyogenes more commonly cause are mechanisms of other classes of antibiotics. In addition, drownings and poisonings remain common causes of morbidity and mortality in the pediatric population. Poisonings, substance abuse, and child abuse often lead to lifelong medical and social consequences. This morning, she is found comatose 21 years sustain traumatic head injuries while and resuscitation is unsuccessful. Helmet use while bicycling prevents related to Ecstasy have been linked to which of what percent of serious brain injury A 4-year-old boy has just fallen off the top rung (C) Henoch-Schoenlein purpura of the ladder while climbing up to the 3-m (D) idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. He lands on the pavement and is motionless when (E) child abuse the lifeguard arrives there in less than a minute. A 4-year-old boy was found playing with an and anemia open bottle of drain cleaner about 1 hour ago. The parents state the (B) closely observe the child and bring to child initially had some gagging and coughing the emergency room if condition and within an hour developed labored breath worsens ing. A 3-year-old child who is unresponsive pres ents with weakness, excessive salivation, brady 18. A teenager who sniffs spot remover and then (D) a hydrocarbon engages in stressful physical activity is at risk for (E) an organophosphate (A) convulsions (B) hypertension 15. Which of the following sets of blood gas values (E) fracture of the humerus is most compatible with acute aspirin poison ing in a 16-month-old child Hyperventilation due to salicylate poisoning (E) fireworks (A) is apparent on physical examination within minutes of ingestion (B) is characterized by an increase in rate and depth of ventilation 186 8: Injuries, Poisoning, and Substance Abuse 28. A 1-year-old child is brought to the emergency (A) necrosis at the site of the bite room because of a swollen left thigh. The parents, (B) renal failure who appear very concerned, state they left the (C) hepatic failure child in the care of a newly hired housekeeper (D) muscle cramps and seizures early that morning, and when they returned (E) convulsions home in the evening they noted the swelling. X-ray examination coal may be indicated in the overdose of which discloses a displaced fracture of the shaft of the of the following A 2-year-old child is retrieved from a near (B) order a complete coagulation profile drowning episode in a pool. On arrival in the emergency room, abnor (D) order calcium, phosphate, and uric acid malities which of the following are most likely laboratory tests to be present and require immediate attention Syrup of ipecac should be administered in the (D) acidosis and hypoxemia home to which of the following children The child suddenly comes upstairs, screaming (A) Children, beyond the age of 1 year, or of being bitten by a spider. The most likely complication in this seat-belted adult is almost as safe as in child would be which of the following Which of the following statements regarding unintentional (nonabuse) injuries in children Concerning child sexual abuse, which of the the categories of injuries from most common to following is correct Which of the following statements regarding (B) lead firearm-related injuries in children less than 19 years of age is correct For each question, match the one lettered option that is most closely associ ated with the question. A history of unconsciousness, irritability and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and lethargy, amnesia for the event, and/or vom hematologic abnormalities generally are present iting are seen commonly in the absence of major and suggestive of the diagnosis. Although neurologically impaired encountered in children with respiratory symp children are at increased risk for abuse, most toms; radiographs can be normal initially. This is given as vomiting is associated with an increase understandable, considering the mechanism of risk for aspiration and subsequent respiratory poisoning. Some children will midal symptoms typical of phenothiazine toxic chronically ingest the paint flakes. This improvement, how endoscopic evaluation is indicated, it should be ever, typically is short-lived, necessitating repeat performed within the first 24 hours because of dosing. These are classified Treatment is supportive; in severe cases, mechan as illicit or banned substances and include, among ical ventilatory assistance may be required. It combines with iron to through the continental United States and many form ferrioxamine, which is excreted in the other countries. A lethal arrhythmia then is pre adult, often results in an epiphyseal fracture in a cipitated by the catecholamine release occa child. In adolescents and adults, the predominant not licensed for use in the United States but early abnormality usually is the respiratory alka readily available from dealers for less than $5 losis. This compound can be obtained in rhages are characteristic of the abusive head small quantities at large parties or in liter bottles trauma syndrome. Proof is not a prerequisite for report two doses of activated charcoal in the treatment ing. In this case, further eval tion, some drugs undergo enterohepatic or uation by scanning, or blood tests are not neces enteroenteric recirculation which, in the case of sary since the fracture is clearly seen on plain an overdose, may be enhanced by such ther films. Further, it cations to its use, and the potential of other alter recommends safe disposal of all ipecac from native therapies. Caregivers of a acute brain swelling are the major causes of child who may have ingested a toxic substance morbidity and mortality. Aspiration pneumo should consult with local poison control centers by nia is common. Envenomation is characterized by severe large quantities of fluid, therefore, is rare. This is followed by a second cannot give consent or activities that violate stage of deceptive quiescence, of up to 48 hours, the laws and taboos of a society. Of children and ado cord marks on buttocks), delay in seeking med lescents who survive near-drowning, an esti ical attention, a history that changes during the mated 35% will have significant neurologic course of the evaluation, and a history of recur impairment. The are related to six categories of health-risk story the parents gave that the child fell forward behaviors: violence, tobacco use; alcohol and into the water in a pot on the stove is inconsistent other drug use; sexual activity that contribute with the pattern of burn. These behaviors fre quently are interrelated and are established during childhood and adolescence and extend into adulthood. The average smoker in the United States starts at age 12 years and most are regular smokers by age 14 years. Adolsecent smokers may become nicotine dependent after smoking fewer cigarettes than adults. While cigarettes are the most common tobacco products used by adolescents, cigars and smokeless tobacco use is common (11% and 6% respectively). Cotinine is the major metabolite of nicotine and can be Figure 8-1 detected in urine. History of injury may cide account for approximately 70% of all not be elicited, and physical findings often are deaths in this age group. Among adults aged >25 years, 59% of all deaths in the United States result from cardiovascular disease (36%) and cancer (23%). Young children are less every 8 hours based on his pharmacokinetics prone to develop hepatic injury following acet from the last admission. Tobramycin levels aminophen overdoses compared to adults due obtained appropriately after the third dose are: to which of the following You also note (A) administering the diazepam via intra a bald patch with a similar-looking lesion on the muscular route scalp. Which of the following medications is (B) administering the diazepam via the most appropriate treatment for this patient A 3-year-old girl presents to your clinic with (A) intranasal pseudoephedrine spray 5 days of rhinorrhea, cough, and congestion. What is the most appropriate coun (E) cromolyn sodium seling to give this mother regarding over-the counter medication usage in children You are in the delivery room for the birth of a (A) All over-the-counter medications are safe. The heart rate is found to have a combination of medications that be less than 60 beats per minute. The decision can have serious side effects in children, is made to place an endotracheal tube and always consult a physician for dosing mechanically ventilate the newborn. You the following locations is the use of a local anes noticed in physical examination that the patient thetic with epinephrine contraindicated A 4-year-old boy presents to the primary care initiate albuterol via nebulizer, oral steroids, clinic with a complaint of cough. Her medication regimen is (E) daily systemic corticosteroids currently phenytoin twice daily. His (E) corticosteroids mother has a note from his teacher that your patient frequently misbehaves in class, gets up 13. A 9-year-old boy with Duchenne muscular dys ing with magazines and toys when you try to trophy presents to the pediatric emergency talk to him. The decision is made to intubate most appropriate medication to offer this the patient for respiratory failure. The vomiting for 2 days, there are other sick con seizure lasts less than 15 minutes. After the the following drugs can decrease the rate of medication is given, the patient begins to recurrence of febrile seizures He admits (B) nitroglycerin to drinking water from a pump-well he found with his older brother. Which of the following drug should (D) dobutamine you administer for treatment of acute nitrate (E) milrinone poisoning Which of the following antibiotics would be most appropriate for pro (C) akinetic seizures phylaxis against bacterial endocarditis On fur (E) vancomycin ther history you determine the family has a problem with mice and rats and have rodenti 24. Which of the fol lowing is most appropriate for the treatment of (C) copper sulfate Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
Depressed women may experience an overconcern for Startle the baby fungus gnats poison buy mycelex-g 100mg cheap, guilt antifungal body soap generic 100 mg mycelex-g visa, or feelings of inadequacy antifungal wiki order discount mycelex-g online. Psychiatric features include nervousness fungus nail medicine 100 mg mycelex-g visa, fatigue antifungal antibacterial soap buy cheap mycelex-g 100mg on line, insomnia fungi definition kingdom purchase mycelex-g without prescription, mood lability, and dysphoria. Symptoms can include prominent, generalized anxiety symptoms, Panic attacks, or obsessions or compulsions. Prominent anxiety, Panic Attacks, or obsessions or compulsions predominate in the clinical picture. There is evidence from the history, physical examination, or laboratory findings that the disturbance is the direct physiological consequence of a general medical condition. Specify if: With Generalized Anxiety: if excessive anxiety or worry about a number of events or activities predominates in the clinical presentation With Panic Attacks: if Panic Attacks predominate in the clinical presentation With Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms: if obsessions or compulsions predominate in the clinical presentation Coding note: Include the name of the general medical condition on Axis I. Questions Symptoms can range from generalized anxiety symptoms (worry, restlessness, etc) to panic attacks (discrete periods of intense fear or discomfort) to obsessions or compulsions. There must be evidence from the history, physical examination, or laboratory findings that the disturbance is the direct physiological consequence of a general medical condition. The diagnosis of an anxiety disorder due to a general medical condition cannot be made if the symptoms can be accounted for by another mental disorder. The disturbance must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. This link must be made with some relative certainty, in order for the diagnosis to be accurate. Q: Is there any evidence of recent or prolonged substance use (including medications with psychoactive effects) The use of many illicit substances such as amphetamines, marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, alcohol, and prescription medications may lead to symptoms of anxiety. Questions the diagnosis of substance-induced anxiety disorder may be more appropriate. There must be a prominent general medical condition for the diagnosis of anxiety disorder due to a general medical condition. In primary anxiety disorders, there is typically no specific and direct causative physiological mechanism associated with the onset of the anxiety symptoms. A variety of general medical conditions may cause anxiety symptoms, including endocrine conditions (thyroid disease, pheochromocytoma, etc), cardiovascular conditions (congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, etc), respiratory conditions (pneumonia, hyperventilation, etc), metabolic conditions (porphyria), and neurological conditions (neoplasms, encephalitis, etc). Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of any medical conditions that may cause anxiety or panic attacks The plaintiff with Specific Phobia experiences a marked and persistent fear of a clearly discernible object or situation. Plaintiffs claiming a specific phobia often have an early history of childhood fears, including school phobia. Marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable, cued by the presence or anticipation of a specific object or situation. Exposure to the phobic stimulus almost invariably provokes an immediate anxiety response, which may take the form of a situationally bound or situationally predisposed Panic Attack. Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging. The phobic situation(s) is avoided or else is endured with intense anxiety or distress. The anxiety, Panic Attacks, or phobic avoidance associated with the specific object or situation are not better accounted for by another mental disorder, such as Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Familial conditions are more common in bio Familial logical relatives, and may have pre-existed the cause of action. In the case of Pattern Specific Phobia, fears of blood and injury have a particularly strong familial pattern. The plaintiff suffers from an immediate anxiety response in the form of a situationally bound or situationally predisposed panic attack. The plaintiff may try to avoid the situation or if not possible, he/she may endure it with intense anxiety or distress as described above. In many cases, the anxiety and avoidance behaviors would have pre-existed the cause of action. Questions If the witness indicates the possibility of other life stressors or other conditions, see (continued) the section on life stressors for further questions. A panic disorder is characterized by discrete periods of panic or intense anxiety. Between attacks, the plaintiff is anxious, worried, and fears having another attack. Panic symptoms include dizziness, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, smothering or choking sensations, feelings of unreality, tingling in hands or feet, hot and cold flashes, sweating, faintness, trembling or shaking, and the fear of dying or going crazy. The plaintiff typically avoids crowds, being outside alone, General standing in line, crossing a bridge, or riding in a vehicle. Agoraphobia is the fear and avoidance of places and situations in which the plaintiff would be unable to escape or get help if s/he had embarrassing symptoms. Symptoms of a limited agoraphobic attack may include dizziness or falling, depersonalization or derealization, loss of bladder or bowel control, vomiting, and cardiac distress. The avoidant plaintiff is characterized by social inhibition or discomfort, fear of negative evaluation, and timidity, along with a great desire for companionship and guarantees of uncritical acceptance. The plaintiff may be easily hurt by disapproval, exaggerate potential difficulties or dangers, and fear being embarrassed or hurt by others. This disorder is diagnosed only after the behavior has persisted for many years and the plaintiff is at least 20 years old. The paranoid plaintiff has a history of unwarranted suspicion and mistrust of others. The plaintiff with social phobia or social anxiety disorder, fears situations in which s/he may be scrutinized by others or in which s/he may do something humiliating or embarrassing. The plaintiff avoids or endures with intense anxiety situations such as public speaking, eating or writing in front of others, using public toilets, or answering questions in social situations. Questions the schizoid plaintiff is introverted, withdrawn, and prefers to be alone. S/he (continued) tends to be indifferent to social relationships and has few close friends outside the family. In addition, panic attacks may be observed in certain nonpsychiatric medical conditions. In some persons, the fear of having a panic attack becomes associated with certain situations, most commonly, using public transportation, driving across a bridge, being in a crowd, waiting in line, or leaving familiar settings alone. There are many alternate causes for panic attacks and the numerous symptoms related to this disorder. Both (1) and (2): (1) recurrent unexpected Panic Attacks (See linked section) (2) at least one of the attacks has been followed by 1 month (or more) of one (or more) of the following: (a) persistent concern about having additional attacks (b) worry about the implications of the attack or its consequences. A discrete period of intense fear or discomfort, in which four (or more) of the following symptoms developed abruptly and reached a peak within 10 minutes: (1) palpitations, pounding heart, or accelerated heart rate (2) sweating (3) trembling or shaking (4) sensations of shortness of breath or smothering (5) feeling of choking (6) chest pain or discomfort (7) nausea or abdominal distress (8) feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint (9) derealization (feelings of unreality) or depersonalization (being detached from oneself) (10) fear of losing control or going crazy (11) fear of dying (12) paresthesias (numbness or tingling sensations) (13) chills or hot flushes Note: Attacks involving four or more symptoms are panic attacks; attacks involving fewer than four symptoms are limited symptom attacks (see Agoraphobia Without History of Panic Disorder). First-degree biological relatives of Familial individuals with Panic Disorder are up to 8 times more likely to develop Panic Pattern Disorder (reference 7, p. Questions Panic disorder is characterized by the presence of recurrent, unexpected panic attacks followed by concern about having other panic attacks. Panic attacks are characterized by discrete periods of intense fear or discomfort with varying degrees of symptomology which develop abruptly. If the witness indicates that the fear between attacks is not associated with having another attack, the plaintiff may be experiencing generalized anxiety disorder and not panic disorder. Q: Does the plaintiff have concern about having another attack, worry about the implications of the attack or a change in behavior related to the attack Along with recurrent unexpected panic attacks, at least one of the attacks in one month must be accompanied by concern about another attack, worry about the implications of the attack and/or a change in behavior related to the attack. It is very difficult for any clinician to determine the cause of panic attacks, with any degree of certainty, without the completion of a thorough medical examination, blood-work including a thyroid study and a cardiovascular examination. Later in the illness certain situations may become so associated with panic attacks that the likelihood of having an attack increases, but the plaintiff can not be certain when an attack will occur or if it will occur at all. If the witness indicates that the attacks occur immediately before or on exposure to a situation that almost always causes anxiety, the plaintiff may have a specific phobia. The witness must indicate the occurrence of at least four panic symptoms during one attack. Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of intense anxiety and panic before the injury in question A child with an overanxious disorder has excessive or unrealistic anxiety or worry for at least six months. Symptoms include muscle tension, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbance, and irritability. Intoxication with the following substances may cause an organically based anxiety syndrome and anxiety symptoms. Asthma is a chronic and episodic illness, characterized by widespread narrowing of the tracheobronchial tree. Psychiatric forces may affect the clinical expression of asthma in several ways: altered awareness of airway resistance, suggestibility to airway constriction, and comorbidity with panic disorder and depression. Accelerated Q: When and how often does the plaintiff experience palpitations or accelerated Heart Rate heart rate Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of any medical or psychological conditions that may cause palpitations or accelerated heart rate The symptoms may become so severe that the plaintiff feels incapacitated and quits working. The plaintiff may also complain of chest pain, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, blurred vision, and flushing. Headaches will occur in about one-third of moderate to high caffeine consumers when their daily intake is stopped. Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of any medical or psychological conditions that may cause sweating The plaintiff may develop recurrent unilateral vasodilatory headaches after recovering from an acute injury involving the anterior triangle of the neck. These headaches may also produce pupil dilation, tearing, sweating, nausea, vomiting, and photophobia. Cluster headaches are characterized by severe unilateral pain in the eye or temple. Flashbacks of experiences may recur several months or years after hallucinogen use. Unlike schizophrenics, (continued) they are able to talk in detail about their hallucinations. Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of trembling or shaking before the injury in question It typically begins before age 25 and persists throughout life gradually spreading to other parts of the body. Conversion symptoms are defense mechanisms that change the unconscious emotional conflict into a physical disability that often symbolizes the nature of the conflict. The plaintiff often has exaggerated and vague complaints focusing on either organs or types of symptoms such as pseudoneurologic or conversion Shaking symptoms, gastrointestinal, female reproductive, psychosexual, pain, and (continued) cardiopulmonary symptoms. These signs, often resembling influenza symptoms, may be precipitated by the abrupt ending of one or two weeks of continuous opioid use. During epileptic seizures, or convulsive attacks, the plaintiff may experience a loss of consciousness and motor control (jerking of all extremities). It often produces personality changes, confusion, dizziness, tremor, anxiety, tachycardia, and sweating during acute attacks. Symptoms may include tremor exaggerated with movement, difficulty speaking and swallowing, incoordination, personality changes, explosive anger, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, memory loss, and dementia. Chorea is characterized by irregular, jerky, and varied involuntary movements when the plaintiff is at rest. Other symptoms may include nausea, diarrhea, polyuria (the passage of an excessive quantity of urine), polydipsia (excessive thirst), and weight gain. The plaintiff may experience anxiety, dementia, irritability, dizziness, fatigue, headache, vomiting, tremor, hyperthermia (high body temperature), and changes in appetite and personality. Caution: Do not ask the following question if the cause of action involves a head injury or toxic exposure. Organic brain syndrome is a term for the symptoms produced by head injury, toxic exposure, hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), anoxia (extreme oxygen deficiency in tissues) or other causes. Common symptoms of head injuries include vertigo, syncope (faint) lightheadedness, trembling, impaired concentration and memory, easy fatigability, irritability, lack of energy, depression, anxiety, phobia, a lowered tolerance for alcohol, and headaches. The plaintiff that consumes one Shaking gram per day usually experiences more severe symptoms. Products which contain (continued) caffeine include: coffee, tea, soda, chocolate and weight-loss aids. Breath, Q: When and how often does the plaintiff experience a shortness of breath or Smothering smothering sensations Sensations Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of shortness of breath before the injury in question Q: Does the plaintiff have a history of any medical or psychological conditions that may cause shortness of breath or smothering sensations Heart pounding, palpitations, and tachycardia are often associated with indigestion, overexertion, a specific emotion, or fatigue. The plaintiff often has exaggerated and vague complaints focusing on either organs or types of symptoms such as pseudoneurologic or conversion Breath, symptoms, gastrointestinal, female reproductive, psychosexual, pain, and Smothering cardiopulmonary symptoms. Anxiety, depression, suicide attempts, social Sensations withdrawal, and work or interpersonal relationship difficulties are common. Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness and dyspnea (shortness of breath). Plaintiffs with chronic psychogenic breathlessness may be depressed or have a reactive depression to stress.
Order genuine mycelex-g on line. Best lazer toe nail fungus Treatment.
Human Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors Are a Target of the Marine Toxin 13 Desmethyl C Spirolide fungus network generic mycelex-g 100 mg online. Separating the grain from the chaff: particle selection in suspension and deposit-feeding bivalves fungus gnats larvae kill order mycelex-g 100mg without prescription. Regional and seasonal differences in light absorption by yellow substance in the Southern Bight of the North Sea fungus gnats cinnamon purchase mycelex-g 100mg on line. The Anthropocene is functionally and stratigraphically distinct from the Holocene fungus gnats roses order mycelex-g no prescription. Harmful algal blooms and climate change: Learning from the past and present to forecast the future antifungal pet shampoo buy mycelex-g. A review and new analysis of trophic interactions between Prorocentrum minimum and clams antifungal ketoconazole purchase mycelex-g 100mg visa, scallops, and oysters. Experimental and Histological Studies of Four Life-History Stages of the Eastern Oyster, Crassostrea virginica, Exposed to a Cultured Strain of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Conversion of eicosapentaenoic acid to chain-shortened omega-3 fatty acid metabolites by peroxisomal oxidation. Production of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide by the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. Inhibition of egg hatching success and larvae survival of the scallop, Chlamys farreri, associated with exposure to cells and cell fragments of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. The effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, vitamins and trace metals on the growth of the red tide organism Prorocentrum micans. The phenoloxidase activity and antibacterial function of a tyrosinase from scallop Chlamys farreri. Computation of nitrate concentrations in turbid coastal waters using an in situ ultraviolet spectrophotometer. The Haber-Bosch process, in particular, enabled an intensification of the global fertilizer use, resulting in higher crop yields across the world. Yet, due to the inefficient incorporation of fertilizers into agricultural products, these nutrients led to significant environmental pollution and eutrophication. During these events, a phytoplankton species is able to proliferate at the expense of others, causing severe harm to the environment through hypoxia, shading, physical disruption and the release of potent toxins. In addition to regular sampling campaigns, we identified several knowledge gaps in the available literature that we first had to resolve in order to answer this main question. In particular, we needed to determine whether changes in the total or relative nutrient availability, both effects of eutrophication, affect the competitive traits of potentially harmful dinoflagellates. Next, we needed to verify that climate-change driven temperature increases would not affect these traits either. To this end, we measured the density, nutrient concentrations and toxin production of 300 single and mixed cultures of Prorocentrum lima, P. Overall, the external nutrient stoichiometry had little effect on the growth and toxin production of our species. As a result, the N:P ratio was found to have no structuring role in the competition between dinoflagellates with closely resembling nutrient requirements. Chapter 3 explores how initial densities may shape the outcome of interspecific competition between dinoflagellates, and whether conditions such as temperature, nutrient availability and nutrient stoichiometry are able to change this outcome. Two large-scale culture experiments were set up using the common dinoflagellate species Alexandrium minutum, Prorocentrum micans and Protoceratium reticulatum. The first experiment applied different macronutrient concentrations (total nutrient availability) and multiple N:P ratios (relative nutrient availability) to verify the results of chapter 2. The second experiment varied the initial community compositions of the cultures by changing the relative species densities at the start, and included abiotic variability as different temperatures and N:P ratios. Again, we monitored the densities and nutrient levels of these 468 cultures for over a month. We found that the community dynamics could be predicted using only the nutrient uptake rates, conversion efficiencies and the maintenance requirements of each individual species. Abiotic variability like temperature, nutrient stoichiometry and nutrient availability affected the parameter estimates, but did not change the underlying mechanism of the competition. Overall, this study demonstrated how initial densities may overturn the outcome of bloom development, giving credit to the importance of cyst beds in the marine environment, and shows that the pre-bloom competition between dinoflagellates is nutrient driven, illustrating the need to need to restrict the nutrient inputs into the North Sea. To this end, we used the common blue mussel as a model organism, a true North Sea ecosystem engineer on its own. In chapter 4, we investigated how the exposure to multiple toxic algae affects the feeding of adult mussels. In addition, we looked at the absorption, distribution, metabolization and excretion kinetics of their toxins. More specifically, we exposed adult mussels to the dinoflagellates Alexandrium ostenfeldii and Prorocentrum lima, in a single and combined two-week laboratory exposure. Both experiments revealed a rapid accumulation of okadaic acid, dinophysis toxins and spirolides in the visceral tissues of M. Worryingly, the simultaneous exposure to both algae increases the rate of the accumulation and metabolization processes, and led to the creation of different metabolized compounds. By exposing mussel embryos to various concentrations of dissolved toxins and their producers, the toxic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries and the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima, we found a previously unknown toxic effect of okadaic acid, which was attributed to its ability to inhibit larval protein phosphatase. Yet, while we found several previously unknown toxicity effects of dinoflagellates, we found no compelling evidence of strong interactions between both stressors. Overall, we concluded that the main effects of each stressor is separated in time. Still, we believe that these interactions can occur at a later stage, once bivalves are large enough to consume pathogens and harmful dinoflagellates at the same time. In addition to more research on the nutrient competition between co-occurring phytoplankton, and the potential for harmful effects on key stone bivalve species, we highly recommend the development of a coherent plankton monitoring network in our coastal zone. Dankzij het Haber-Bosch proces is het gebruik van meststoffen sterk toegenomen in de afgelopen 50 jaar, met een hogere landbouwopbrengst tot gevolg. Door de inefficiente opname van nutrienten door de gewassen, komt een groot deel van deze kunstmeststoffen terecht in het grond en oppervlaktewater, wat eutrofiering en milieuvervuiling veroorzaakt. De afgevloeide nutrienten komen via sloten, beken, kanalen en rivieren uiteindelijk in de zeeen en oceanen terecht, waar ze de chemische balans van het water verstoren. Dit proces heeft geleid tot een globale toename in het voorkomen van schadelijke algenbloei. In dit proefschrift proberen we dit the bereiken aan de hand van verschillende multifactoriele langetermijnstudies met relevante modelorganismes. Naast regelmatige bemonsteringen van het zeewater, identificeerden we belangrijke ecologische vragen in de beschikbare literatuur die we dienden the beantwoorden in functie van ons doel. Zo was het nodig om the weten in welke mate de totale en relatieve beschikbaarheid, beide gewijzigd door eutrofiering, een effect hebben op het competitief gedrag van schadelijke algen in het huidig en toekomstig klimaat van de Noordzee. Daarnaast zijn we nagegaan of schadelijke pantserwieren of dinoflagellaten het voorkomen van ziektes in sleutelsoorten als de mossel Mytilus edulis kunnen verhogen. Daarvoor werden 300 enkelvoudige en gemengde kweken van vier veelvoorkomende dinoflagellaten Prorocentrum lima, P. De densiteit, nutrienten concentraties en toxine productie werd gedurende een maand opgevolgd. Algemeen beschouwd, bleek uit dit experiment dat de N:P ratio weinig effect heeft op de groei en de toxine productie van dinoflagellaten. Extra stikstof veroorzaakte veelal wel een verhoging in de densiteit van de algen. De ontwikkeling en competitie in de celculturen verliep meestal sneller bij hogere temperaturen. Twee grote, multifactoriele kweekexperimenten werden gebruikt om na the gaan wat het effect van nutrienten concentraties, de N:P ratio, temperatuur en de densiteit van verschillende soorten is op de uitkomst van de competitie tussen de dinoflagellaten. Alexandrium minutum, Prorocentrum micans en Protoceratium reticulatum, gekweekt bij verschillende nutrienten concentraties en N:P verhoudingen. In het tweede experiment varieerden we zowel de N:P ratio, als de temperatuur en de initiele samenstelling van de gemengde culturen. Tijdens beide experimenten werd opnieuw gekeken naar het verloop van het aantal cellen en de nutrienten concentraties. Abiotische variantie zoals temperatuur, de N:P verhouding en de totale beschikbaarheid aan nutrienten hadden elk een invloed op deze parameters, maar veranderden niets aan het onderliggende mechanisme van de competitie. Met dit werk werden het belang van cysten en nutrient concentraties in de Noordzee, en de preventieve maatregelen met betrekking tot beide, nogmaals onderstreept. Naast het verlies van biofiltratie, verhoogt dit namelijk het belang van planktonische grazers die zich niet voeden op toxische algen. In hoofdstuk 4 werd onderzocht hoe de blootstelling aan meerdere giftige algen het voedingsgedrag van de mossel kan beinvloeden. Daarbij werd gekeken naar de absorptie, distributie, metabolisatie en excretie van de toxines. Volwassen mosselen werden gedurende twee weken onder labo condities enkel of gelijktijdig blootgesteld aan Alexandrium ostenfeldii en Prorocentrum lima. Daarnaast werden mosselkooien in de haven van Oostende geplaatst, om de opname van toxines onder natuurlijke omstandigheden the bestuderen. Gedurende beide experimenten werden regelmatig toxine profielen geregistreerd met vloeistofchromatografie met massaspectrometrie. Zowel de natuurlijke blootstelling als de labo experimenten veroorzaakten een snelle toename in toxines (vnl. Tijdens de gelijktijdige blootstelling aan de algen nam de accumulatiesnelheid toe, en werden zelf andere metabolieten gevonden. Deze studie toont dus aan dat mengsels van ongereguleerde toxines voorkomen aan onze kust. Hoofdstukken 5 en 6 spitsen zich toe op de impact van giftige algen op de larven van de mossel. In hoofdstuk 5 onderzochten we eerst of de twee meest abundante toxines (domoizuur en okadazuur) en hun producenten, Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries en Prorocentrum lima, een effect hebben op de ontwikkeling, overleving en immuun activiteit van deze gevoelige levensstadia. Daar werd ontdekt dat okadazuur een onbekende toxiciteit vertoont in mossellarven, die we verbonden aan de inhibitie van fosfatase activiteit. Daarnaast werd waargenomen dat elke andere behandeling een immuunrespons veroorzaakte, waardoor het immuunsysteem van de larve mogelijk onderdrukt wordt. Dit laatste is zorgwekkend omdat mariene pathogenen reeds een ernstige bedreiging vormen voor mosselpopulaties. Hierdoor kunnen in de toekomst steeds vaker mengsels van deze stressoren opduiken in het mariene milieu. Om na the gaan wat de mogelijke gevolgen zijn natuurlijke schelpdierpopulaties, werden in hoofdstuk 6 mossellarven blootgesteld aan diverse giftige wieren (Alexandrium minutum, A. De ontwikkeling, overleving en immuun respons van de mossel larven werd opnieuw geregistreerd. Daaruit bleek dat verscheidene pantserwieren een dusver ongekende impact hebben op de overleving van mossellarven maar, desondanks de individuele effecten van beide pathogenen, er geen sterkte interacties bestaan tussen deze twee stressoren. Ook het primitieve immuunsysteem kon onafhankelijk reageren op zowel de bacterien als de toxische pantserwieren. Desalniettemin vrezen we dat deze interacties toch een rol kunnen spelen zodra de mossel groot genoeg is om zich gelijktijdig the voeden op toxische algen en bacterien. Naast een voortzetting van het onderzoek naar de competitie in natuurlijk gemeenschappen van algen, raden we de verdere ontplooiing van een planktonmonitoring netwerk ten stelligste aan. Dissertation: the introduction of artificial markers into the genome of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Involvement Mentored 13 B. Diel variation in feeding and movement patterns of juvenile Atlantic cod at offshore wind farms. In vivo X-ray elemental imaging of single cell model organisms manipulated by laser-based optical tweezers. Methodological challenges of optical tweezers based X-ray fluorescence imaging of biological model organisms at synchrotron facilities. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry-based screening reveals lipophilic toxins in multiple trophic levels from the North Sea. The combined temperature and nutrient load effects do not explain the development of harmful algal blooms. Shifting N:P ratios do not affect the competitive traits of dinoflagellates under present and future climate change scenarios. International workshop on the sustainable use of coastal and marine resources in Kenya: from research to societal benefits, Kikambala, Kenya, 27-29 October, 2014. Synchrotron Radiation X-ray Fluorescence Imaging of Biological Model Organisms Manipulated by Laser-Based Optical Tweezers. In vivo x-ray elemental imaging of single cell model organisms manipulated by laser-based optical tweezers. In vivo x-ray elemental imaging of biological model organisms manipulated by laser based optical tweezers. In vivo x-ray elemental imaging of single cell model organisms manipulated by laser based optical tweezers. Non contact optical tweezers-based single cell analysis through in vivo X-ray elemental imaging. Reconstruction of the 3D full elemental profile of Ceriodaphnia dubia using multimodal registration approaches. European Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry, Sankt Anton, Austria, 19-24 February 2017. Full lines represent the mean prediction, dashed lines are 95% confidence intervals.
During the therapy the patient is encouraged to experience a series of what Janov calls primal diabet-x antifungal purchase mycelex-g mastercard, in which the patient relieves the prototypical traumatic events that originally crystallized his suffering and thereby created his neurosis fungus gnats allergic reaction buy generic mycelex-g canada. Primary process: In psychoanalysis fungus mulch purchase genuine mycelex-g, the mental activity directly related to the functions of the id and characteristic of unconscious mental pro cesses fungus gnats aquarium gravel 100mg mycelex-g with mastercard. The primary process is marked by privative xifaxan fungus 100 mg mycelex-g, prelogical thinking and by the tendency to seek immediate discharge and gratification of instinctual demands fungus gnats cinnamon cheap mycelex-g 100mg amex. Principal diagnosis: the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for the admission of the patient to the hospital or for outpatient treatment. Principle of closure: Probably the most powerful of the Gestalt principles of perceptual organization, the principle of closure refers to the perceptual tendency towards complete forms and shapes. So a set of disconnected lines is likely to be seen as indicating an incomplete shape if this is at all possible, rather than simply being taken as independent stimuli. The principle of closure also extends into the perception of movement, in the form of stroboscopic motion and the phi pheno menon. Principle of proximity: One of the Gestalt principles of perceptual organizations, which states that stimuli which occur close to one another will tend to be perceived as grouped together, all other things being equal. Principles of similarity: One of the Gestalt principles of perceptual organization which states that similar will tend to be perceived as grouped together, all other things being equal. Prison psychosis: Psychotic reaction to incarceration or to the prospect of incarceration. Privilege: Legal term referring to the legal right of a patient to prevent his physician from testifying about information obtained in the course of treatment. In some states, infor mation obtained in the course of the doctor-patient relationship is considered privileged communi cation. Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences 325 Privileged communication: the laws of evidence in some jurisdictions provide that certain kinds of communication between persons who have a special confidential or fiduciary relationship will not be divulged. The psychotherapist-patient and doctor-patient relationship is, in some states, considered privileged communication. It is important to realize that the privilege belongs to the patient not to the therapist, and can be waived only by the patient unless otherwise provided by the law of legal proceedings. Proactive interference: When information which has already been learned interferes with the learning of new material. Proactive interference is parti cularly common when someone is trying to learn a set of similar tasks within a relatively short period of time. Process schizophrenia: Unofficial term for schizo phrenia attributed more to endogenous factors than to specific environmental influence. It often serves as a warning or premonitory sign of the approach of a morbid condition. Programmed learning: A technique for applying operant conditioning to classroom learning. The information is broken down into small units, and presented to the student in such a way that one unit leads naturally on to the next. If the student gets it right, they move onto the next state; if they get it wrong, they go back over the relevant material again. The idea is that this approach maximizes positive reinforcement (in the shape of correct answers) for the student, thus maximizing interest in and application to the learning process. As an example of pure operant conditioning, 326 Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences programmed learning has been criticized on the grounds that knowledge of results is a cognitive rather than a behavioural reinforcement. In class room practice, the absence of social interaction between student and teacher has often presented its own difficulties, and programmed learning has tended to be introduced in a manner that is far more limited than was previously envisaged. Projection: Unconscious defense mechanism in which a person attributes to another those generally un conscious ideas, thoughts, feelings, and impulses that are in himself undesirable or unacceptable. By externalizing whatever is unacceptable the person deals with it as a situation apart from himself. Projective set: A type of psychological test with loosely structures test material that requires the subject to reveal his own feelings, personality, or psycho pathology. Prosocial behaviour: the opposite of antisocial beha viour; prosocial is used to refer to behaviour which involves helping others or making a positive gesture towards them in some way. It is commonly used in discussions of bystander intervention and altruistic behaviour. Prosopagnosia: An inability to recognize familiar faces that is not due to impaired visual acquity or level of consciousness. Prototaxic: A term introduced by Harry Stack Sullivan to refer to primitive illogical thought processes. Pseudo aggression: A neurotic defense in which the patient denies his basic masochistic feelings and displays them, instead, as false aggression. Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences 327 Pseudo collusion: Sense of closeness, relationship, or cooperation that is not real but is based on trans ference. Pseudocyesis: It is defined as the conviction of a non pregnant woman that she is pregnant, occurring with symptoms associated with pregnancy. It excludes delusions of pregnancy during psychosis, feigned pregnancy in malingering, endocrinal disorders like the galactorrhoea amenorrhoea syndrome and pelvic or abdominal tumors causing symptoms of pregnancy. Pseudodementia: A dementia-like disorder that can be reversed by appropriate treatment and is not caused by organic brain disease. The term is also used to describe a condition in which the patient shows an exaggerated indifference to his surroundings in the absence of a mental disorder. Pseudofamily: See Care-giver Pseudologia fantastica: A disorder characterized by uncontrollable lying in which the patient elaborates extensive fantasies that he freely communicates. Pseudo mutuality: Phenomenon displayed by married couples and families in which the members are united by their capacity to satisfy each others neurotic needs. Pseudoschizophrenia: A group of disorders resembling schizophrenia in some of their clinical features but belonging to different diagnostic categories. Psychasthenia: Obsolete term used by Janet to describe a syndrome characterized by fears and phobia. The psychoanalytical literature, following Freud, uses psyche and mind synony 328 Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences mously. Psychiatrist: A medical doctor whose speciality is the study and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatry: the branch of medicine that deals with diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mental dis orders. Psychic determinism: Freudian concept that all mental phenomena have specific antecedent causes, often operating on an unconscious level. Psychoanalysis: A theory of human mental phenomena and behaviour, a method of psychic investigation and research, and a form of psychotherapy origi nally formulated by Sigmund Freud. As a technique for exploring the mental processes psychoanalysis includes the use of free association and the analy sis and interpretation of dreams, resistances, and transferences. Psychoanalysis is also known as analysis in depth and its practitioners are known as psychoanalysts. Psychoanalyst: A psychotherapist, usually a psychia trist, who has had training in psychoanalysis and who uses its techniques in a treatment setting. Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences 329 Psychoanalytic group psychotherapy: A method of group psychotherapy pioneered by Alexander Wolf and based on the operational principles of individual psychoanalytic therapy. Although strictly designating treatment structures to produce significant char acter change, the term encompasses the same approach in groups conducted on more superficial levels for smaller goals. Psychobiology: Term introduced by Adolf Meyer and referring to the study of the human being as an integrated unit, incorporating psychological, social and biological functions. Moreno in which personality make-up, inter personal relationships, conflicts, and emotional problems are expressed and explored through dramatization. The therapeutic dramatization of emotional problems includes (1) protagonist or patient, the person who presents and acts out his emotional problems with the help of (2) auxiliary egos, persons trained to act and dramatize the different aspects of the patient that are called for in a particular scene in order to help him express his feelings, and (3) the director, leader, or therapist, the person who guides those involved in the drama for a fruitful and therapeutic session. Psychodynamics: the systematized knowledge and theory of human behaviour and its motivation the study of which depends largely upon the functional significance of emotion. Psychogenic amnesia: A dissociative disorder charac terized by the sudden inability to recall information stored in memory in the absence of an underlying organic mental disorder. When associated with travel to another locate and the assumption of a new identity, the condition is called psychogenic fugue. Psychogenic dysmenorrhoea: Abdominal pain or cramps occurring during menstruation (and not as part of the premenstrual tension syndrome), for which underlying psychological causes have been postulated without being convincingly demonstra ted. In the absence of gastrointestinal disease, last for several days and cease abruptly, with a tendency to reoccur after intervals of several weeks or longer. Psychogenic fugue: A dissociative disorder charac terized by periods of total amnesia in which one travels and assumes a new identity. Psychogenic hiccough, psychogenic cough: Hiccough (singultus), the involuntary spasm of the inspi ratory muscles followed by an abrupt closure of the glottis, can be a normal transient occurrence after eating or drinking or, when persisting or reoccurring frequently, a symptom of a somatic disease. Psychogenic cauzation has been surmised, but not proved, in cases where no physical cause is found. In contrast, a dry, unproductive cough in the absence of respiratory or central nervous system disease, is more readily accepted to be a neurotic symptom or an isolated psychogenic tic. Psychogenic pain disorder: A disorder in which the predominant feature is the complaint of pain on Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences 331 the absence adequate physical findings and in which there is evidence that psychological factors play a causal role. Psychohistory: As approach to history that examines events within a psychological framework. If attempts to connect individual and collective ideas and emotions with wider historical currents. Psychokinesis: Phenomenon in which directed thought processes influence physical events. Psycholexicology: the psychological study of words and their meanings (believed to be coined by Geroge A. Psycholinguistics: the exploration of the psycho logical factors involved in the development and use of language. Psychologist, clinical: A psychologist with additional training and experience in a clinical setting who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of human mental disorders. Psychometry: the science to testing and measuring mental and psychologic ability, efficiency poten tials, and functioning, including psychopathologic components. Psychomotor agitation: Generalized physical and emotional overactivity in response to internal and/ or external stimuli, as in hypomania. Psychomotor retardation: Slowing of mental and physical activity, common in depression. Psychopolitics: A relatively new term that has been applied in two different contexts. According to one usage, it describes the psychological dimension of political behaviour, such as the reciprocal influence on persons of political environments and their societies. According to another image, it refers to specific tactics of politicians that are intended to yield benefits to them through the use of psychological strategies. With resolu tion of this interaction, a balanced, reality-oriented development takes place; with disturbance, fixation and conflict ensure. This disturbance may remain latent or give rise to character logic or behavioural disorders. The stages of development are: (a) Oral: the earliest of the stage of infantile psychosexual development, lasting from birth to 12 months or longer. Usually subdivided into two stages: the oral erotic, relating to the pleasurable experience of sucking, and the oral sadistic, associated with aggressive biting. Both oral eroticism and sadism continue into adult life in disguised and sublimated forms, Dictionary of Psychology & Allied Sciences 333 such as the character traits of demandingness or pessimism. Oral conflict, as a general and pervasive influence, might underlie the psychologic determinants of addictive dis orders, depression, and some functional psychotic disorders. The child must desexualize the relationship to both parents in order to retain affectionate kinship with both of them. With this internalization largely completed, the regulation of self-esteem and moral behaviour comes from within. Pyschosexual disorder: A disorder of sexual functioning that is caused, wholly or partly, by psychological factors. See also Ego-dystonic homosexuality, Gender identity disorder, Paraphilia, Psychosexual dysfunction. Psychosexual dysfunction: A psychosexual disorder characterized by an inhibition in sexual desire or a psychophysiological functions.
References
- Sisley K, Rennie IG, Parsons MA, et al. Abnormalities of chromosomes 3 and 8 in posterior uveal melanoma correlate with prognosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1997;19(1):22-28.
- Hearn JWD, AbuAli G, Reichard CA, et al. HSD3B1 and resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer: a retrospective, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol 2016;17(10):1435-1444.
- Snyder M, Renaudin J. Intracranial hemorrhage associated with anticoagulation therapy. Surg Neurol 1977;7:31.
- White JJ, Kaback MM, Haller JA Jr: Diagnosis and excision of an intrapericardial teratoma in an infant. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1968; 55:704-710.
- Mahajna A, Aboud N, Harbaji I, et al. Blunt and penetrating injuries caused by rubber bullets during the Israeli-Arab conflict in October, 2000: a retrospective study. Lancet 2002;359:1795- 1800.
