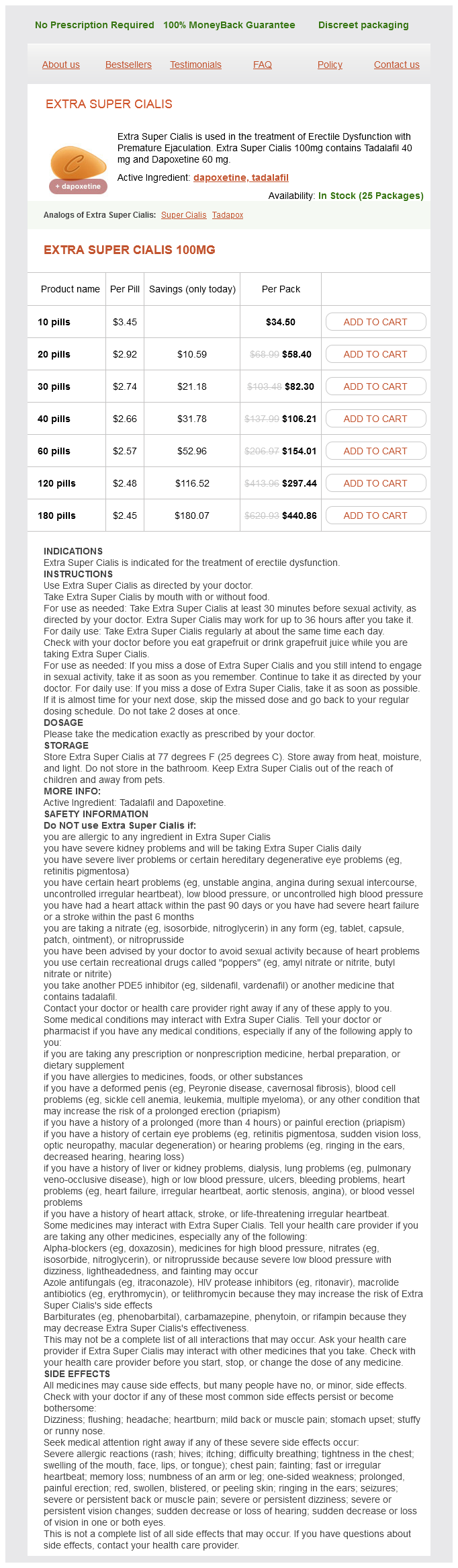
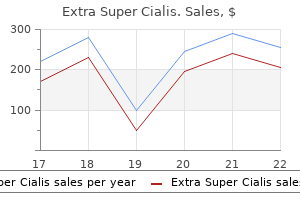
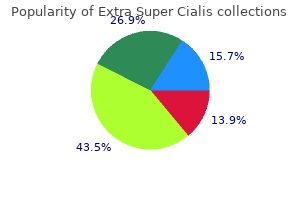
Extra Super Cialis
Chirag V. Patel, MD
- Assistant Professor of Radiology
- UC Davis Medical Center and Children's Hospital
- Sacramento, California
It is necessary to teach depend on his interaction with similar-age peers how to get the attention of the child peers and/or siblings erectile dysfunction age onset buy extra super cialis uk. This gives the have a lower rate of initiating social interac peers opportunities to use the skills they have tions with peers than with adults erectile dysfunction can cause pregnancy purchase 100 mg extra super cialis otc. As the school professional erectile dysfunction treatment perth 100 mg extra super cialis free shipping, your role is to provide prompts and feedback to facilitate interaction between both groups causes of erectile dysfunction include safe extra super cialis 100mg. The older brothers successfully used prompting (verbal and physical) and reinforcement (verbal and tangible) sublingual erectile dysfunction pills buy cheap extra super cialis on-line. It is important to keep certain factors in mind while you design peer training inter ventions erectile dysfunction hiv proven extra super cialis 100 mg. In addition, the activities you include in the session should address the interests and preferences of both groups of students. You should expect challenges with both maintenance and generalization of the targeted skills, and should focus on addressing these challenges. Both methods teach skills in the natural environment and create situa tions in which the student will be motivated to learn. Because we want them to be independent, we do not want children to wait passively for other people to make positive situations occur. Pivotal Response Treatment: Has been shown to be effective for children aged 3-9 years Is associated with favorable outcomes for children diagnosed with autism Has been shown to be effective with target skills and behaviors, including: Communication skills Interpersonal skills Play skills Consider the following examples of Pivotal Response Treatment: Example 1: Communication is one of the most critical skills to target for students with autism. These strategies include: varying the materials used during teaching to avoid boredom; using natural reinforcers and making sure they are available for attempts at communication; and teaching in the natural environment. For instance, students on the autism spectrum are less likely to pretend that a plastic plate is a hat, or that a play stove is hot. Instead, if they engage in appropriate play, they are more likely to use a toy exactly as it was designed to be used. When improvements in symbolic play were noted, the student was expected to demonstrate more creative play. By using these strategies, children between the ages of 4 and 7 were taught to engage in more symbolic play (Stahmer, 1995). These strategies have also been used to improve sociodramatic play (an advanced form of symbolic play that includes skills like role playing, social interaction, etc. In this case, the peers learned these strategies during recess over the course of seven consecu tive days. When watching a movie, you might not want to know Transitions may be better managed exactly what will happen. A student situations, we like to have an idea of who does not enjoy academic work may what to expect. Predictability in life is beneft from an intervention in which generally comforting to us all. First he completes the ling you; or the administrative assistant academic work and then he gets access started singing tunes to the school over to a preferred activity. These situations can add more pictures as he masters seem unreasonable and unpredictable, the use of the schedule and can toler and would leave us uncomfortable, to ate increased demands before he gains say the least! Educators have used various this is because it is hard for them to pick media such as pictures (real photos or up on the subtle cues which signal to the Boardmaker), written or typed docu rest of us that something in the environ ments, or 3-D objects. The goal is to the board and placing it in a done/ 61 } Evidence-based Practice and Autism in the Schools completed/fnished bin/bucket/box/pile. Some schedules also include photos of the staff involved in the activ ity, location details, and materials that are needed. Some students set their schedule once a day; others set their schedules in the morning and again in the afternoon. Some educators may make the schedule for the student or with the student; others allow students to make their own schedules. In all instances, indi vidualization is the key to ensuring the student benefts completely from the schedule. In one study, students (7-8 years old) were taught to use visual schedules to transition to and from four learning cen ters in a classroom (writing, reading, listening, and art center). To help the students transition successfully, they used pictures in a photo album in the order in which the activities were expected to occur. For instance, picture schedules have been developed with Velcro placed on the back of each picture. The student can be taught to match the picture on the schedule to the picture on the container that includes his work material. Teachers with tasks in which adult supervision is may partner with parents to develop not needed, accepted, nor expected. If you photographic activity schedules target have ever been on and off a diet, tried to ing leisure, social interaction, self-care, improve your exercise habits, or endeavored and housekeeping tasks. Schedules can to build more activities into your schedule, be presented in a three-ring binder with then you have probably tried to improve one photograph per page. In one case, a your self-regulation through the use of Self student was taught to point to the page, management procedures. A dependent individual, on the other hand, is Self-regulation limited in the range of social and general life A student who uses self-management is experiences he is afforded. Their inability to pick up when a task is accurately completed (Pierce on these subtle cues and alter their behavior & Schreibman, 1994). Self-management can accordingly will impede their success in many be used to teach the student to perform steps situations. Benefts of Self-management include: Building awareness of your behavior Accountability for carrying out a procedure Direct and immediate self-feedback when recording your own data Multi-tasking. When a student frst learns a new skill, instructors may need to use one of the other active teaching strategies, such as live or video modeling. Once the student learns each component of a task, he needs to evaluate his own efforts to determine if he has accurately completed each component of the task. In order to learn to evaluate his efforts, he needs to have: Clear criteria established so he knows when he has succeeded and when he has fallen short of the mark. He might keep track of his performance using checklists, wrist counters, velcroed smiley faces that move from the incomplete column to the completed column of a task list, or any num ber of other strategies geared toward his interest. Almost everyone who starts evaluating his performance on a task records inaccurate data (intentionally or unintentionally). Instructors often need to give prompts (verbal and non-verbal cues) so students can learn to correctly self-record their behavior. National Autism Center { 64 this neutral, qualifed person could Example 2: Self-management can be anyone in the school system who enhance the independent completion of understands the self-management tasks. They frst need to focus on dom in our lives, we all need to learn to rewarding accuracy in recording and independently complete a number of daily not get side-tracked by inaccuracies in living tasks. Often, the adult retains control over the One way to do this is to create a photo reinforcers. Students with gain access to the reinforcer (Pierce and existing schedules can often be taught to Schreibman, 1994). For instance, one of your students important for both long-term health and may already follow a schedule to transition as a natural way for students to actively from one activity to the next. He may not engage in leisure activities in their com yet have developed the skill to determine munities. Self-management can be used when any of the activities are completed to teach students to track their physical accurately, or perhaps he cannot yet activity. Reinforcers can be provided for arrange for access to reinforcers to main completing a set amount of exercise or tain his efforts. You should plan to systematically fade adult or external, overt cues used during self-management. In some cases, it may be necessary to continue using prompts over a relatively long period of time in order to achieve a desirable level of self-management across new behaviors. Story-based Intervention Package Story-based interventions are similar to written scripts and Self-management in that they involve written materials that are designed to increase independence. You can follow the stories with discussion or comprehension questions to make certain the student understands the main points. Students often receive reinforcement for reading the story and performing the behavior correctly. In addition, the stories are sometimes used to prompt the student in the natural environment. However, if a child has strong listening comprehension skills, you might read the story to her instead of having her read it independently. Consider the example of an adolescent who makes girls uncomfortable because he stares at them. His teacher writes a story in which the student learns to look at girls only briefy and then look away from them. His looking at girls now more closely parallels the behavior of his fellow classmates, and the girls may be more comfortable in his presence (Scattone, Wilczynski, Edwards, & Rabian, 2002). The Social Story was paired with prompting and reinforcement in the form of praise. The students each improved their ability to make choices without a great deal of teacher prompting. They also went from spending no time playing appropriately during cen ter activities to spending a minimum of 5-15 minutes playing appropriately. Although a great deal more research is necessary to determine whether numer ous interventions can lead to favorable outcomes, scientists have already conducted enough research to show that many interventions are effective. The great news is that there are now 11 Established Treatments that have suffcient research support to demonstrate they are effective. The overwhelming majority of these interventions were developed in the behavioral literature. Importantly, several interventions were also infuenced by felds such as special education and developmen tal psychology. This is one of the reasons professional judgment (Chapter 3) and family input (Chapter 4) are essential. We hope the upcoming chapters clarify the roles of professional judg ment and family input in the delivery of evidence-based practice in the schools. It is not possible to develop systematic capacity to deliver research-supported treatments without frst understanding the information contained in the present chapter. Steps to independence: Teaching practices for children with autism: everyday skills to children with special Educational and behavior support interven needs. Teaching Treatment of autism spectrum disorders: children with autism: Strategies for initiat Evidence-based intervention strategies for ing positive interactions and improving communication and social interactions. Antecedent assessment & intervention: Supporting children & adults with developmental disabilities in com munity settings. Establishing use of Evaluation of a vocal mand assessment and vocal descriptive adjectives in the spontaneous speech mand training procedures. Liquid on-schedule behaviors to high-functioning chil rescheduling for the treatment of rumination. The effects of echolalia on acqui intensive behavior analytic and eclectic treat sition and generalization of receptive labeling ments for young children with autism. Teaching symbolic play engagement with peers and stereotypic skills to children with autism using pivotal behavior of children with autism. An implicit normal educational and intellectual func technology of generalization. Teaching autism to self-monitor their social interac children with autism to respond to joint tions: An analysis of results in home and attention initiations. Self-management of schedule social communication of school-age chil following in three teenagers with autism.
Peripheral Iridotomy erectile dysfunction and diabetes discount extra super cialis 100 mg free shipping, Iridectomy impotence group purchase extra super cialis 100 mg, and Iridoplasty Pupillary block in angle-closure glaucoma is most satisfactorily overcome by forming a direct communication between the anterior and posterior chambers that removes the pressure difference between them injections for erectile dysfunction cost extra super cialis 100 mg free shipping. A ring of laser burns on the peripheral iris contracts the iris stroma erectile dysfunction doctor type order extra super cialis with paypal, mechanically pulling open the anterior chamber angle erectile dysfunction band purchase 100mg extra super cialis overnight delivery. The technique is applicable to many forms of open-angle glaucoma erectile dysfunction signs cheap extra super cialis uk, and the results are variable depending on the underlying cause. The pressure reduction usually allows decrease of medical therapy and postponement of glaucoma surgery. Laser trabeculoplasty may be used in the initial treatment of primary open-angle glaucoma. Glaucoma Drainage Surgery the increased effectiveness of medical and laser treatment has reduced the need for glaucoma drainage surgery, but surgery is able to produce a more marked reduction in intraocular pressure. The major complication is fibrosis in the episcleral tissues, leading to closure of the new drainage pathway. This is most likely to occur in young patients, in blacks, in patients with secondary glaucoma, and in those who have previously undergone glaucoma drainage surgery or other surgery involving the episcleral tissues. Perioperative or postoperative adjunctive treatment with antimetabolites such as 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C (in low dosage) reduces the risk of bleb failure and is associated with good intraocular pressure control but may lead to bleb-related complications like persistent ocular discomfort, bleb infection, or maculopathy from persistent ocular hypotony. Implantation of a silicone tube without a valve (Baerveldt or Molteno tube) or with a valve (Ahmed valve) to form a permanent conduit for aqueous flow out of the eye is an alternative procedure for eyes that are unlikely to respond to trabeculectomy. Viscocanalostomy and deep sclerectomy with collagen implant avoid full-thickness incisions into the eye. The intraocular pressure reduction is not as good as that achieved with trabeculectomy, but there is less potential for complications. There are a number of novel surgical procedures for glaucoma, including microelectrocautery to ablate a strip of trabecular meshwork, micro-stents, and canaloplasty, that result in modest reduction of intraocular pressure without the formation of a bleb, but as yet, there are no long-term results and no randomized trials. Goniotomy and trabeculotomy are useful techniques in treating primary congenital glaucoma, in which there appears to be an obstruction to aqueous drainage in the internal portion of the trabecular meshwork. Cyclodestructive Procedures Failure of medical and surgical treatment in advanced glaucoma may lead to consideration of laser or surgical destruction of the ciliary body to control intraocular pressure. Treatment is usually applied externally through the sclera, but endoscopic laser application systems are available. The disease is four times more common and six times more likely to cause blindness in blacks. There is a strong familial tendency in primary open-angle glaucoma, and close relatives of affected individuals should undergo regular screening. The consequence is a reduction in aqueous drainage leading to a rise in intraocular pressure. Juvenile-onset open-angle glaucoma (a familial primary open-angle glaucoma with early onset), about 5% of familial cases of primary open-angle glaucoma, and about 3% of nonfamilial cases of primary open-angle glaucoma are associated with mutations in the myocilin gene on chromosome 1. Raised intraocular pressure precedes optic disk and visual field changes by months to years. Although there is a clear association between the level of intraocular pressure and the severity and rate of progression of visual loss, there is great variability between individuals in the effect on the optic nerve of a given pressure elevation. Nevertheless, higher levels of intraocular pressure are associated with greater field loss at presentation. When there is glaucomatous field loss on first examination, the risk of further progression is much greater. Since intraocular pressure is the only treatable risk factor, it remains the focus of therapy. There is strong evidence that control of intraocular pressure slows disk damage and field loss. For each 1-mm Hg reduction of intraocular pressure, there is an approximately 10% decreased risk of progression of glaucoma. If there are extensive disk changes or field loss, it is advisable to reduce the intraocular pressure as much as possible, preferably to less than 15 mm Hg. A patient with only a suspicion of disk or field changes may need less vigorous treatment. In all cases, the inconveniences and possible complications of treatment must be considered. In order to gain a perspective on the need for treatment, an initial period of observation without treatment may be necessary to determine the rate of progression of disk and field changes. There is no justification for subjecting an elderly patient to extremes of treatment when the likelihood of their developing significant visual loss during their lifetime is small. Diagnosis the diagnosis of primary open-angle glaucoma is established when glaucomatous optic disk or field changes are associated with raised intraocular pressures, a normal-appearing open anterior chamber angle, and no other reason for intraocular pressure elevation. At least one-third of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma have a normal intraocular pressure when first examined, so repeated tonometry can be helpful. Screening for Glaucoma the major problem in detection of primary open-angle glaucoma is the absence of symptoms until relatively late in the disease. When patients first notice field loss, substantial optic nerve damage has already occurred. If treatment is to be successful, it must be started early in the disease, and this depends on an active screening program. Unfortunately, glaucoma screening programs are hampered 536 by the unreliability of a single intraocular pressure measurement in the detection of primary open-angle glaucoma and the complexities of relying on optic disk or visual field changes. At present, it is necessary to rely for early diagnosis predominantly on regular ophthalmologic assessment of first-degree relatives of affected individuals. Course & Prognosis Without treatment, open-angle glaucoma may progress insidiously to complete blindness. If antiglaucoma drops control the intraocular pressure in an eye that has not suffered extensive glaucomatous damage, the prognosis is good (although visual field loss may progress despite normalized intraocular pressure). When the process is detected early, most glaucoma patients can be successfully managed medically. Trabeculectomy is a good option in patients who progress despite medical treatment. The pathogenesis may involve an abnormal sensitivity to intraocular pressure because of vascular or mechanical abnormalities at the optic nerve head, or this may be a purely vascular disease. There may be an inherited predisposition, with normal-tension glaucoma being particularly common in Japan. A few families with normal-tension glaucoma have an abnormality in the optineurin gene on chromosome 10. Some studies have shown associations with vasospasm and low intracranial pressure. Before the diagnosis of normal-tension glaucoma can be established, a number of entities must be excluded: 1. Prior episode of raised intraocular pressure, such as caused by anterior uveitis, trauma, or topical steroid therapy. Large diurnal variation in intraocular pressure with significant elevations, 537 usually early in the morning. Intermittent elevations of intraocular pressure, such as in subacute angle closure. Other causes of optic disk and field changes, including congenital disk abnormalities, inherited optic neuropathy, and acquired optic atrophy due to tumors or vascular disease. Among patients diagnosed with normal-tension glaucoma, approximately 60% have progressive visual field loss, suggesting the possibility of acute ischemic events in the pathogenesis of those without progression. Reduction of intraocular pressure is beneficial in patients with progressive visual field loss, but this may not be achieved with medical therapy. The possibility of a vascular basis for normal tension glaucoma has led to the use of systemic calcium channel blockers, but definite benefit from this intervention has yet to be demonstrated. The risk increases with increasing intraocular pressure, increasing age, greater optic disk cupping, a positive family history for glaucoma, and perhaps myopia, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. The development of disk hemorrhages in a patient with ocular hypertension also indicates an increased risk for development of glaucoma. Patients with ocular hypertension are considered glaucoma suspects and should undergo regular monitoring (once or twice a year) of intraocular pressures, optic disks, and visual fields. It is likely that many ocular hypertensives who do not develop glaucoma have relatively thick corneas, producing an overestimation of intraocular pressure. Measurement of central corneal thickness may therefore be useful to determine which patients are at risk 538 of developing glaucoma. Conversely, many individuals with ocular hypertension may have glaucoma, but the retinal ganglion cell damage is not detectable with currently available techniques. Developments in perimetry and retinal nerve fiber layer imaging are addressing this issue. Elevation of intraocular pressure is a consequence of obstruction of aqueous outflow by occlusion of the trabecular meshwork by the peripheral iris. The condition may manifest as an ophthalmic emergency or may remain asymptomatic until visual loss occurs. The diagnosis is made by examination of the anterior segment and careful gonioscopy. Primary angle-closure glaucoma is the term that should be used only when primary angle closure has resulted in optic nerve damage and visual field loss. Risk factors include increasing age, female gender, family history of glaucoma, and Southeast Asian, Chinese, or Inuit ethnic background. This blocks aqueous outflow, and the intraocular pressure rises rapidly, causing severe pain, redness, and blurring of vision. Angle closure develops in hyperopic eyes with preexisting anatomic narrowing of the anterior chamber angle, usually when it is exacerbated by enlargement of the crystalline lens associated with aging. This occurs spontaneously in the evenings, when the level of illumination is reduced. It may be due to medications with anticholinergic or sympathomimetic activity (eg, atropine for preoperative medication, antidepressants, nebulized bronchodilators, or nasal decongestants). The patient should be advised to seek attention immediately in the event of ocular pain or redness or increasingly blurred vision. Clinical Findings Acute angle closure is characterized by sudden onset of visual loss accompanied by excruciating pain, halos, and nausea and vomiting. Other findings include markedly increased intraocular pressure, a shallow anterior chamber, a steamy cornea, a fixed, moderately dilated pupil, and ciliary injection. It is important to perform gonioscopy on the fellow eye to confirm the anatomic predisposition to primary acute angle closure. Differential Diagnosis (see Inside Front Cover) Acute iritis causes more photophobia than acute glaucoma. Intraocular pressure is usually not raised; the pupil is constricted or irregular in shape and the cornea is usually not edematous. Marked flare and cells are present in the anterior chamber, and there is deep ciliary injection. Acute conjunctivitis is usually bilateral, and there is little or no pain and no visual loss. There is discharge from the eye and an intensely inflamed conjunctiva but no ciliary injection. The pupillary responses and intraocular pressure are normal, and the cornea is clear. Complications & Sequelae If treatment is delayed, the peripheral iris may adhere to the trabecular meshwork (anterior synechiae), producing irreversible occlusion of the anterior chamber angle requiring surgery. Pilocarpine 2% should be instilled one-half hour 540 after commencement of treatment, by which time reduction of iris ischemia and lowering of intraocular pressure allow the sphincter pupillae to respond to the drug. Once the intraocular pressure is under control, laser peripheral iridotomy should be undertaken to form a permanent connection between the anterior and posterior chambers, thus preventing recurrence of iris bombe. Surgical peripheral iridectomy is the conventional treatment if laser treatment is unsuccessful. The episodes of angle closure resolve spontaneously, but there is accumulated damage to the anterior chamber angle, with formation of peripheral anterior synechiae. There are recurrent short episodes of unilateral pain, redness, and blurring of vision associated with halos around lights. Examination between attacks may show only a narrow anterior chamber angle with peripheral anterior synechiae. These patients present in the same way as those with primary open-angle glaucoma, often with extensive visual field loss in both eyes. Laser peripheral iridotomy should always be undertaken as the first step in the management of these patients.
The aperture also controls the depth of eld erectile dysfunction caused by ptsd cheap 100 mg extra super cialis fast delivery, which While many nd scales and labels unnecessary refers to the zone of sharpness in front of and distracters in an otherwise aesthetic photograph erectile dysfunction keeping it up buy extra super cialis paypal, behind the point of focus erectile dysfunction clinics buy extra super cialis 100mg free shipping. With large apertures at least one of the specimen photographs should (smaller f-stop numbers) erectile dysfunction aafp order extra super cialis australia, everything outside the include a scale along with the specimen identi plane of focus abruptly becomes blurred erectile dysfunction ed natural treatment purchase extra super cialis overnight delivery. A scale helps the viewer orient small apertures (such as an f-stop of 22) erectile dysfunction operations best buy for extra super cialis, objects the specimen and provides a benchmark for the remain in focus over a greater depth of eld. Commercially prepared plas the amount of light hitting the lm is also tic rulers are available that can be made into vari controlled by the shutter speed. Small adhesive labels with the specimen identi Each shutter speed, like the f-stop, doubles or cation number can be attached directly to the halves the exposure at the next setting. When placing the scale in a photograph, speeds on modern shutters are 1, /2, /4, /8, 1 1 1 1 be sure to place it in the anatomical inferior posi /15, /30, /60, /125 second, etc. The scale should be positioned at the level both the aperture and shutter control the of the specimen so that it is in plane of focus. You need to identify the best f-stops and shut ter speeds for your particular system by running Digital Photography a series of exposure tests for each different speci men magnication. An incident light meter works best because mens, digital images offer several advantages it measures the light falling on the specimen. For example, reected light meters may system permits immediate review of the image read too much of the background and not enough captured. Some digital cameras are also equipped hand-held incident light meter, a series of test with small screens for reviewing the image cap exposures should be made at different magni tured. Most manufactured laboratories that routinely use photography as lenses have reproduction ratios listed on the a component of their gross dissections, digital lens barrel for each magnication. In making this image photography can reduce lm and pro test run, choose a standard exposure such as 1/4 cessing costs. Each month seems to bring an this exposure time will enable you to use small updated digital camera that is less costly and of apertures, which result in a better depth of eld higher quality than the previous model. The are literally hundreds of digital cameras now on best aperture then can be determined for a spe the market, and choosing the best one is a formi cic image magnication, and a chart can be dable task. When selecting a digital camera, one 30 Surgical Pathology Dissection of the most important features to keep in mind one of the two halves. Resolution of interest, use a clean and unassuming probe or has to do with the ability to appreciate ne detail pointer (not a nger). Digital photographs are made up of Fourth, make sure the background is clean and thousands to millions of picture elements known free of distracters. Remember that your work is as pixels, and the quality of an image depends, not over once the photograph is taken. Remove in part, on the number of pixels used to create the specimen, and clean the background so that the image. Conversely, low pixel Dark Specimens numbers obscure ne detail and result in images that have less value for teaching, publication, and Many fresh specimens and bloody specimens documentation of the gross ndings. As a general mind that a high-resolution digital camera is not rule, you can compensate by opening the lens by a substitute for good judgment and technique. This will matter how good the camera, informative images lighten the specimen in the nal photograph. Light Specimens Some Pointers on Photographs of xed specimens can sometimes be bleached white with little or no color informa Photographing Specimens tion. Then take several more photographs General Principles while increasing the f-stop number in half in crements. First, photograph underexposure should provide more detail in the cut surface of the specimen. Section the specimen using a uid sweep Large Specimens ing motion to create a cut surface that is smooth and unrufed. Take the photograph before goug Large specimens generally require at least two ing out tissue for frozen section evaluation or sets of photographs: one of the entire specimen tumor collection; or if these studies are urgently and the other a close-up of the area of interest. Gently rinse blood ner details of a lesion, while the overall view and uid from the surface of the specimen, and will show the relationship of the lesion to the rest then blot the surface of the specimen dry so that of the specimen. Second, decide whether the pathology is best demonstrated in the specimen before or after it Small Specimens is xed. Color is best seen when the specimen is photographed fresh, while ne structural de Most normal lenses will not focus when moved tails are sometimes better appreciated in xed very close. A special macro lens is needed for very small Third, position the specimen so that (1) the area specimens or for close-up photographs to show of interest is centered in the eld of view; (2) its ne detail. The 105-mm macro lens is especially long axis is oriented along the long axis of the suitable for these purposes. It can focus to a point frame; and (3) the specimen lls at least 75% of where the image on the negative is the same size the frame. For bivalved specimens, there is no as the specimen, while maintaining a comfortable need to photograph both halves of the specimen. Also, use a small camera aperture (an tender cable that allows the photographer to f-stop of 22) for increased depth of eld. If the specimen is Oddly shaped specimens are a nuisance to photo fresh, reected light can be reduced by drying graph when they cannot be maintained in the the surface of the specimen with a paper towel. A simple solution is modeling Before tripping the shutter, look through the clay, which can be used to prop up the specimen. Make sure that Mold the clay into shape, and use it as a base to the lighting and arrangement best demonstrate hold the specimen. Small shhooks with nylon cord and Exposure an attached weight can be used to hold areas open. For example, this technique can be useful Once an exposure test has been made and an when photographing the interior of heart valves. The simple solution is to close Under standard lighting conditions, the walls of the aperture. To circumvent this problem, place the the photograph is too dark, simply open the lights as high as possible, so that they illumi aperture so that the lm receives more light. This type of vertical With a little practice and a standard system, you illumination will help reduce shadows as well should be well on the way to top-quality speci as light the entire cavity. Make sure that you are focused on the area of inter est because depth of eld can be a problem. Three-Dimensional Structures Maintenance of the Photography System Side lighting is the best lighting to demonstrate surface detail or to show the three-dimensional Not surprisingly, a system designed for use by quality of a tumor. The lower the angle of the many users is particularly susceptible to abuse light, the more surface relief will be seen. Be raphy system is a daily task that is less likely to careful not to set the lights too low, as this can be neglected if assigned to one person. Reection There is nothing worse than spending valuable time in photographing an important specimen If you are using a piece of glass to support the and afterward nding out that there was no lm specimen, watch out for reections. There is for patients with carcinomas, melanomas, or any practically no role for representative nodal sam other malignant neoplasm with metastatic po pling when searching for metastatic spread. Accordingly, assessment of lymph node lymph node identied should be submitted for specimens is every bit as important as evaluating microscopic examination. If tumor is not grossly visible, the lymph node should be sectioned in 3 to 4-mm slices and all of the sections submitted for microscopic eval Lymph Node Dissections uation. You can slice the lymph node along its long or short axis, but longitudinal sections are generally preferable, as this minimizes the A general approach to sampling lymph nodes is number of slices. No single cassette should described in Chapter 1, and the organ-specic contain slices from more than one lymph node approach to the dissection of regional lymph unless colored inks are used to distinguish nodes is detailed in each organ-specic chapter. For these nonsentinel In this chapter we review a few general guide lymph node dissections, one hematoxylin and lines that can be broadly applied when it comes eosin (H&E)-stained section per tissue block is to evaluating lymph nodes for metastatic disease. Lymph nodes are easiest to appreciate in the fresh state before subtle distinctions in tissue den sity are obscured by tissue xation. Submersion of specimens in certain clearing agents may be help ful in eliminating the bulk of adipose tissue, Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy but this is an unnecessary and time-consuming step that does not improve on meticulous exam ination of the fresh tissues. When appropriate, As noted above, the standard pathologic practice the anatomic levels of the lymph nodes should for the evaluation of nonsentinel lymph nodes is be maintained and separately reported in the sur to examine microscopically one section from each gical pathology report. In cases Although this approach may be practical for where important anatomic landmarks do not evaluating large numbers of lymph nodes, most accompany the specimen, it may not be possible pathologists would concede that such limited to identify levels without the help of the sub analysis consistently underestimates the true in mitting surgeon. Recent im Although tedious, the objective of any lymph provements in our clinical ability to identify the node dissection for metastatic disease is nothing lymph nodes most likely to harbor metastases 34 5. Handling Radioactive Specimens the sentinel lymph node strategy is particularly Obtained by Sentinel Lymphadenectomy appealing because the surgical removal of just one or several selected lymph nodes permits a the processof clinical lymphatic mappingand the more comprehensive pathologic search for small identication of sentinel lymph nodes relies on and localized metastatic deposits. Fortunately Methods for detecting tumor cells in sentinel for pathology personnel, the amount of radiation lymph nodes have become increasingly sophis associated with sentinel lymphadenectomies is ticated and sensitive, ranging from routine low. Even with frequent handling of these speci histologic examination of serial sections to re mens, radiation exposure usually does not ap verse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction proach statutory exposure limits. Given the based methods for detecting a single tumor cell exceedingly low radiation exposure, most au among a sea of lymphocytes. Outside of routine thorities now agree that quarantining these H&E staining, however, most detection methods specimens does not enhance the safety of pathol are investigational, and currently there is no ogy personnel and only serves to delay the nal agreement as to an optimal detection protocol. Accordingly, sentinel lymph node Given the diversity of the processing and exami biopsies should be processed immediately on re nation of sentinel lymph node biopsies among ceipt from the operating room using customary laboratories, you should be familiar with the universal precautions. The sentinel lymph node biopsy specimen Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy should be carefully examined to determine the for Evaluating Metastatic Disease number of lymph nodes. Examine the cut surface of each slice for the the histopathology laboratory cut and stain presence of grossly visible tumor nodules. If tumor is visualized grossly, have the histopathology laboratory cut multi routine H&E staining of a single level is sufcient ple sections from at least three levels. At least to document the presence of tumor and its possi one section from each level should be stained ble extension beyond the lymph node capsule. Additional unstained sections If tumor is not grossly visible, the lymph node should be stored on treated slides for future slices should be sectioned at multiple levels. At a minimum, one section from each of three levels of the tissue Important Issues to Address block should be obtained for routine H&E in Your Surgical Pathology Report staining. The cricoid cartilage is shapedlikeasignetring, anditformstheposterior wall of the larynx. Situated in the back of the the patterns of spread of carcinomas of the larynx larynx are the two arytenoid cartilages. These depend on their site of origin and on well-dened are pyramidal in shape and rest along the upper anatomic barriers. Although the laryngeal anatomy is therefore an essential part hyoid bone is not technically part of the larynx, of the dissection of any laryngeal specimen. The supraglottis is space is lled with fatty connective tissue, and it the portion of the larynx superior to the ventri is bounded posteriorly by the epiglottis, inferi cles. It is composed of the epiglottis, the aryte orly by the thyroepiglottic ligament, anteriorly by noids, the aryepiglottic folds, and the false cords. The paraglottic space is a and their anterior and posterior attachments, the less well-dened area composed of loose connec anterior and posterior commissures. The sub tive tissue, which lies between the thyroid carti glottis begins 1 cm below the free edge of the lage and two membranes that form the structural vocal cords and extends inferiorly to the trachea. The anterior commissure mind throughout your description and dissec is the anterior dense ligamentous attachment tion of the larynx. The important mucosal landmarks to identify the thyroid cartilage lacks an internal perichon in the larynx are illustrated and include the drium; therefore, carcinomas may invade the mucosa of the epiglottis, the aryepiglottic folds, thyroid cartilage at the level of the anterior com the false vocal cords, the ventricles, the true vocal missure. These mucosal surfaces cover nically part of the hypopharynx, one should the cartilaginous framework of the larynx. This be aware of them because they are frequently framework includes the cartilage of the epiglot resected with the larynx. Depending on shaped thyroid cartilage forms the anterior and the size and location of the tumor, laryngeal 38 6. Larynx 39 specimens may also include other portions of the pled margin as precisely as possible. As illus hypopharynx (including the posterior pharyn trated, the superior mucosal margin is formed geal wall and the pharyngo-esophageal junction) (1) anteriorly by the mucosa of the base of the and the thyroid gland. Total Laryngectomy Perpendicular sections of each of these three mu cosal margins should be taken. These can be taken as perpendicu the easiest way to orient a total laryngectomy lar sections from the anterior surface of the speci specimen is to identify the epiglottis. The epiglot men and from any other areas where the soft this is present anteriorly at the most superior tissues appear inltrated by tumor. Keeping the three anatomic then the thyroid cartilage can be used to orient the regions of the larynx (the supraglottis, glottis, specimen. The superior horns of the thyroid carti and subglottis) in mind, carefully document the lage are located superiorly and project poste side, size, and exact location of any tumors. Submit sections of each identied After the specimen has been oriented, ink the tumor for histology to show its maximal depth soft tissue and mucosal margins. The mucosal of invasion as well as its relationship to grossly margins essentially form two rings. Next, carefully examine, ringisformedbythetrachea,andthesuperiorring document, and sample for histology the mucosa isformed bythecircular openingofthe larynxinto of the pyriform sinuses, the epiglottis, the aryepi the pharynx. After the margins have been inked, glottic folds, the false cords, the ventricles, the cut through the posterior wall of the larynx in true vocal cords, the anterior commissure, and the midline using a pair of scissors. In general, longitudinal sections midline approach will fully expose the mucosal are most informative.
Order extra super cialis 100mg overnight delivery. The pharaoh that wouldn't be forgotten - Kate Green.
The potential mechanisms of improve the appearance of the scar by adjusting erectile dysfunction lyrics 100 mg extra super cialis overnight delivery, reposi tioning erectile dysfunction medications that cause extra super cialis 100 mg generic, or narrowing the scar and that complete elimi action are local tissue hypoxia and reduction of the intralesional population of mast cells erectile dysfunction drugs research buy online extra super cialis, which may affect nation of the scar is impossible at this point erectile dysfunction pump how do they work order extra super cialis 100 mg on line. However impotence from priapism surgery best 100 mg extra super cialis, the physician should be sensitive to the fact that the fibroblast growth zma impotence purchase extra super cialis no prescription. Several treatments are Occasionally, psychological counseling should be rec usually required using a low to moderate fluence (5. Hypertrophic scars may also shrink with this treatment as a result of a reduction 2. The technique of resurfacing depends on the theless, in clinical situations, where skin edges are nature of the deformity. The goal of this technique is to grossly misaligned or the scar lies in an unfavorable even out any uneven surfaces. The depth of the derm direction, scar revision may prove beneficial as early as abrasion depends on the depth of the scar. Cosmetically favorable scars are similar tage of laser resurfacing over mechanical dermabrasion is in color to the surrounding tissue. Scars that are advantage is that there is no aerosolization of skin and located in the periphery of the face, at a transition line blood, thereby lowering the risk of viral transmission. The lack of one or more of advantageous in that it produces collagen contracture of these qualities results in an unsightly scar. However, the postoperative period of laser scars are wide, raised, or depressed, or are often hyper resurfacing is marked by prolonged erythema. The most pigmented or hypopigmented compared with the adja common lasers in use for resurfacing are the high-energy cent skin. Good surgical technique is essential for normal hair, and accessories can sometimes offer excellent coverage wound healing. Newer makeup materials and techniques allow too tightly, and cauterizing too excessively may result in for better and more complete coverage of unsightly defects. Opaque cosmetics with a slightly low tone, which disguises Adequate wound humidity and coverage are also the erythema of scars, generally provide better results. Alternately, an M-plasty can be addition, local wound infection prolongs wound heal used at the ends to prevent extending the excision. Bacteria delay normal healing phases by directly scar is excised, the adjacent tissue is undermined, and damaging cells of wound repair by prolonging the the wound is closed with a two-layer closure. Horizon inflammatory phase as well as competing for oxygen tal mattress sutures can be used to enhance wound and nutrients within the tissue. Scars that are perpen fusiform fashion, and the defect is closed in a linear dicular to these lines have the best cosmetic result using fashion. The defect is then closed in two layers, with tion-advancement flaps designed to accomplish three subdermal absorbable sutures to minimize tension and goals: (1) change scar direction, (2) interrupt scar lin fine monofilament sutures, such as 5. Wound ever Z-pasty is particularly beneficial if it can reorient a scar sion should be meticulously achieved. Small and pitted or depressed scars, such as deep acne scars, can be revised by punch excision and pri mary closure with wound eversion. As an alternative, small, full-thickness skin grafts can be placed into the defects and secured in position with sutures, bolstering techniques, or both. A W-plasty, unlike a Z-plasty, incorporates shorter limbs and does not result in an overall change in the length of the scar. This procedure can make the scar less conspicuous by making it irregular and thus more A B C difficult for the observing eye to track. Similarly, with this technique, a long scar replacement of the anterior lamellar defect using a full can be broken up into several smaller components to thickness graft. Finally, scars ophthalmus can be repaired in a similar fashion using that cause distortion of facial features due to scar con skin grafts. In general, they can be used when the such as W-plasty, is that usually no additional normal best option in scar revision is complete excision of the skin needs to be removed. A properly planned Z-plasty scar and reconstruction of the defect with a local flap. For example, a small scar of the nasal tip may be excised Moreover, it can counter the forces of scar contracture, and repaired using a bilobed flap, just as one might thus correcting webbed or contracted scars that distort repair a defect after ablation of a malignant growth in anatomic landmarks. All three limbs are of equal length, and the central limb consists of the Most scars may be improved using a variety of scar revi scar that is to be lengthened and realigned. Essentials of wound care are as impor tion of the final scar can be determined by the direction tant after the revision to achieve optimal outcomes. For long scars for b which a single Z-plasty may produce long, linear scars, 60 a multiple Z-plasties can be used along the scar. The two triangular flaps and the surrounding c tissue are mobilized, and the flaps are transposed and c advanced. After meticulous hemostasis, the flaps are f d closed using tension-reducing techniques and eversion. Skin grafts can also be used to fill skin defects after punch excision of deep or depressed scars. Morphological and immunochemical differences between keloid and hypertrophic scar. Histologic basis of keloid and hyper tensive, comparative study of hypertrophic scars and keloids, trophic scar differentiation. Scar management: prevention and treat scarring and a potential target for anti-scarring gene therapy. Immuno 11735056] (W-plasty provides a regularly irregular scar, and globulin, complement, and histocompatibility antigen studies geometric broken-line closure provides an irregularly irregular in keloid patients. Both methods divert the attention of the eye by produc 432336] (This study suggests that a localized immune response ing a nonlinear scar pattern. This has implications in the aging face in that Facial aging generally consists of intrinsic and extrinsic platysmal bands can form along with the pseudohernia processes. The total the loss of the cervicomental angle, which contributes amount of ground substance, predominantly made of to an aged appearance. In addition, elastic fibers, which maintain the wavy pattern Facial Nerve of collagen bundles, become thin and fragmented with time, beginning at age 30. In a process called elastosis, collagen occurs up to 70% in the zygomatic and buccal branches is degraded and elastin is increased. The dermis becomes and only up to 15% in the frontal and mandibular thickened and poorly organized. Along with fat atrophy rietal fascia and lies just superficial to the superficial layer in the subcutaneous tissue, there is a general redistribution of the deep temporal fascia. The appropriate selection of patients has critical impor Inferiorly, there is continuity with the platysma over the tance in ensuring a desirable outcome. They should be motivated and willing to participate in Platysma other associated changes that support longevity, such as the platysma is a broad, thin muscle innervated by the improved diet, smoking cessation, and sun protection. The cease smoking and stop the use of nonsteroidal anti major concern should be of ptotic skin and muscle. They should be made aware that At the time of the preoperative visit, the procedure rhytidectomy does not stop the aging process but rather should be reviewed, informed consent obtained, and any gives them a more youthful appearance from which they final questions answered. This process is dictated by their mandatory and are taken in the standard lateral, oblique, individual genetic predisposition and somewhat by their and frontal views. However, general anesthesia is Preparation for surgery should include a complete his preferred by many others to maximize patient comfort. Any history of bleeding also allows the surgeon to concentrate on the operative problems should alert the physician that a hematologic field and not have his or her attention distracted by mon workup may be necessary. If the temporal area requires lifting, the incision is curved anterosuperiorly into the hair-bearing scalp. The alternative to bringing the posterior incision Zygomatic along the hairline can result in visible scar tissue from scar widening. Buccal Subcutaneous Rhytidectomy Subcutaneous flap techniques have an extremely low risk Marginal of facial nerve injury and remain in common use. After the induction of general anesthesia, an endotra cheal tube is fixed in the midline, taking care not to dis tort the facial anatomy. The first side is infiltrated with 1% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine along the skin incisions and widely across the planned area of elevation. Adequate local anesthetic is critical in minimizing bleed ing during skin flap elevation through the vasoconstric tive effects of epinephrine. The contralateral side is injected while completing the first side to maximize hemostasis and minimize toxicity. Prior to the adminis tration of anesthesia, care should be taken to calculate the maximal dose, which is based on body weight. The principal goals are to minimize hair loss, hairline adjustments, visible scars, and changes in nor mal anatomic structures. In general, incisions should be placed post-tragal in women and pre-tragal in men. Pre tragal incisions avoid the need to redrape hair-bearing skin onto the tragus. The orly, dissection is carried in a plane superficial to the tem limits of the flap are just below the zygomatic arch poralis fascia, which allows the protection of the frontal superiorly, the anterior border of the parotid gland facial nerve branch. After the exci of hematoma, skin flap ischemia, and facial nerve injury sion of excess tissue, a nonabsorbable suture is used to obviously increase in longer skin flaps. Meticulous hemosta sis of the skin flap is made with bipolar electrocautery Deep-Plane & Composite Rhytidectomy to prevent facial nerve injury. The use of a lighted retractor can help in visualizing bleeding sites, especially Deep-plane rhytidectomy attempts to address aging with longer skin flaps. Anteriorly, the investing fascia is released from use of tissue sealants that use fibrin, thrombin, or plate the zygomaticus major muscle. With experience and a detailed anatomic know the wounds are cleaned and antibiotic ointment is ledge of the facial nerve branches in this area, the surgeon placed on the incisions. Bulky dressings are placed imme may achieve an improved result with this technique. The points of maximal tension are in the temporal and occipital regions and key sutures are placed to suspend the skin flap. Following suspen sion, excess skin is trimmed so that the skin edges are reapproximated in a tension-free manner. This problem can be avoided by incis ing the skin flap so that the lobule rests in a neutral position without tension directed inferiorly. The pretragal area is carefully defatted, and a subcu taneous anchoring suture is placed to recreate the nor mal concave contour of this area. The preauricular and postauricular skin up to the hair-bearing skin is closed with interrupted or running sutures. Closed-suction drainage is placed through a separate stab incision in the hair-bearing skin.
References
- Aretz HT, Billingham ME, Edwards WD, et al. Myocarditis. A histopathologic definition and classification. Am J Cardiovasc Pathol. 1987;1:3-14.
- Wielopolski PA, van Geuns RJ, et al. Breath - hold coronary MR angiography with volume - targeted imaging. Radiology 1998; 209:209.
- Niemela M, Maenpaa H, Salven P, et al. Interferon alpha-2a therapy in 18 hemangioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7:510-516.
- Nehra A, Kumar R, Ramakumar S, et al: Pharmacoangiographic evidence of the presence and anatomical dominance of accessory pudendal artery(s), J Urol 179(6):2317n2320, 2008.
